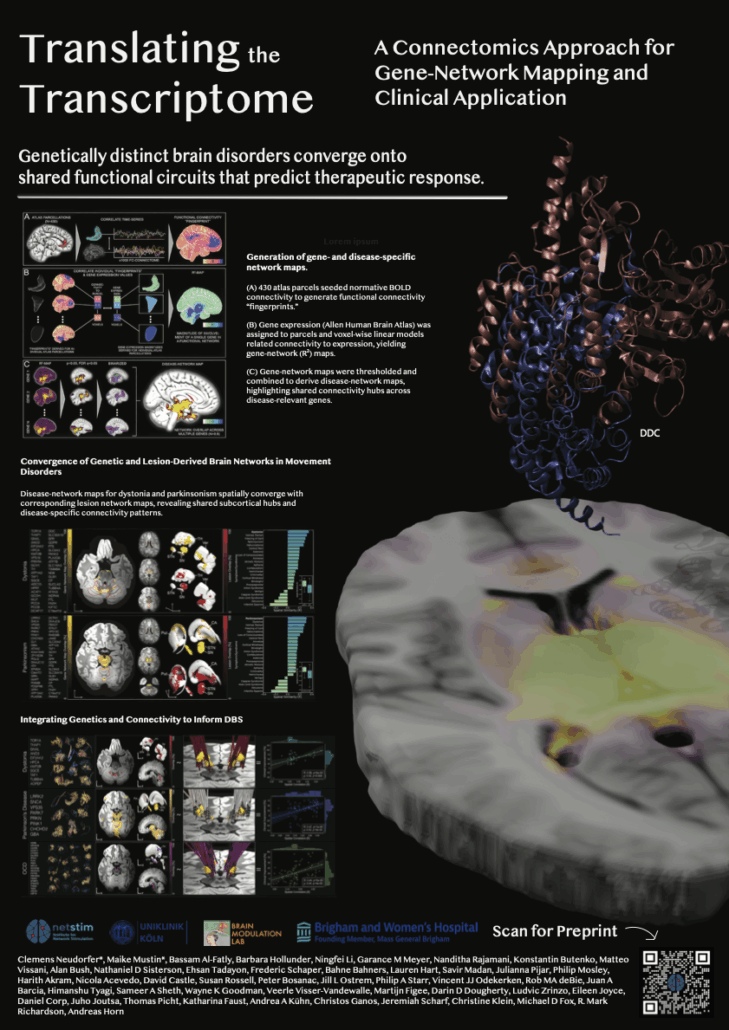
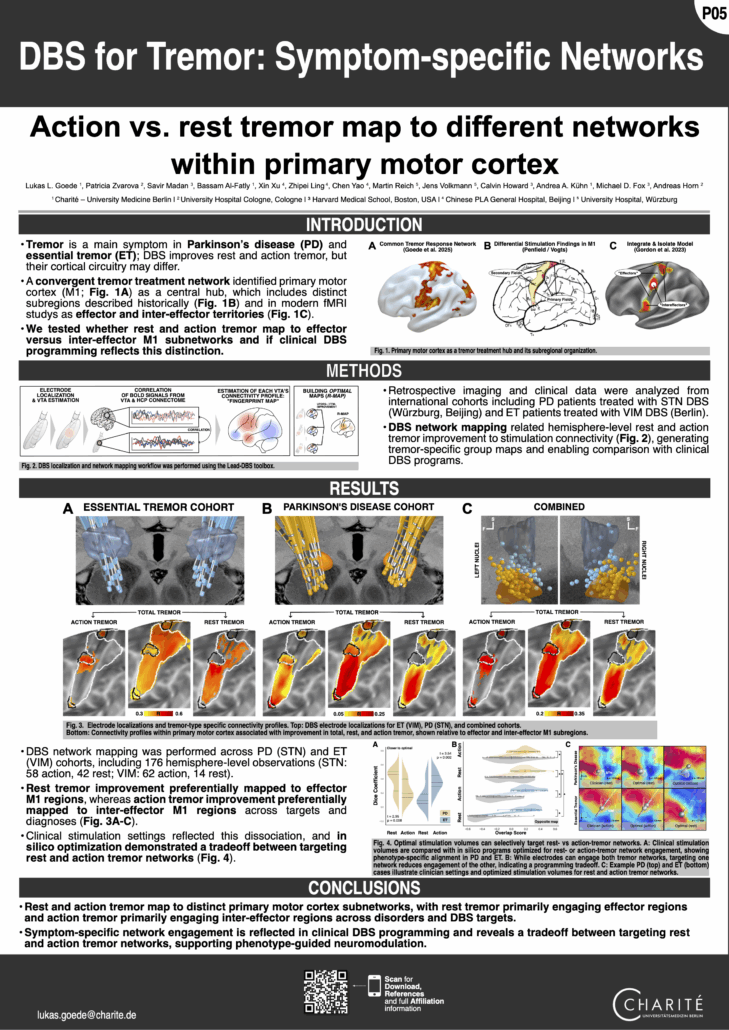
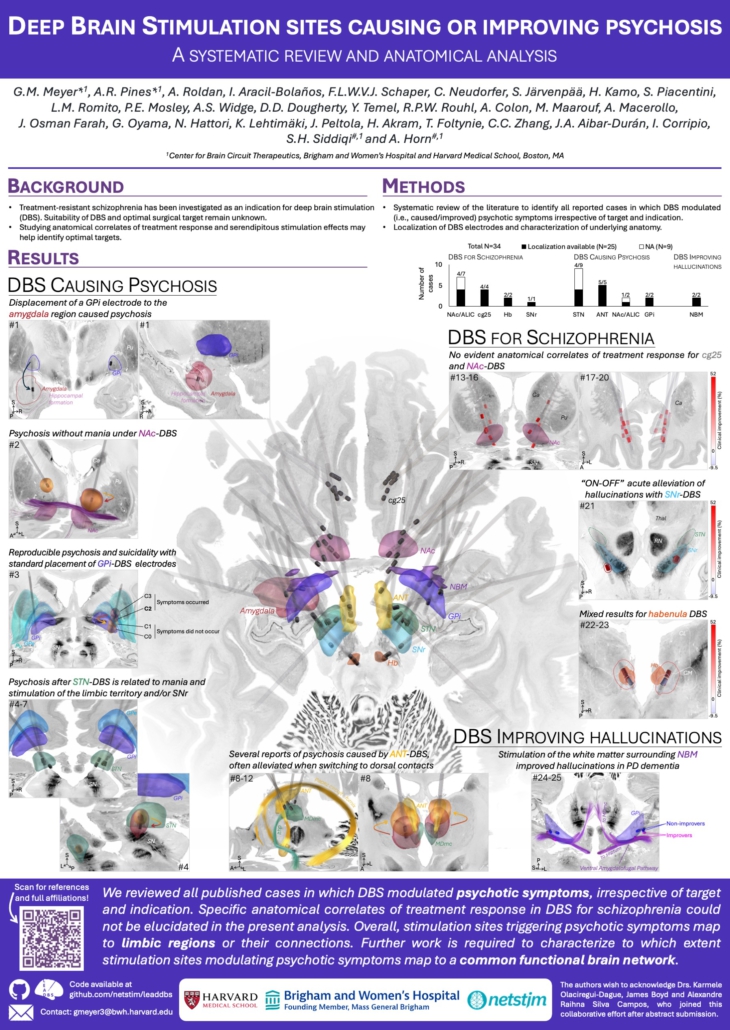
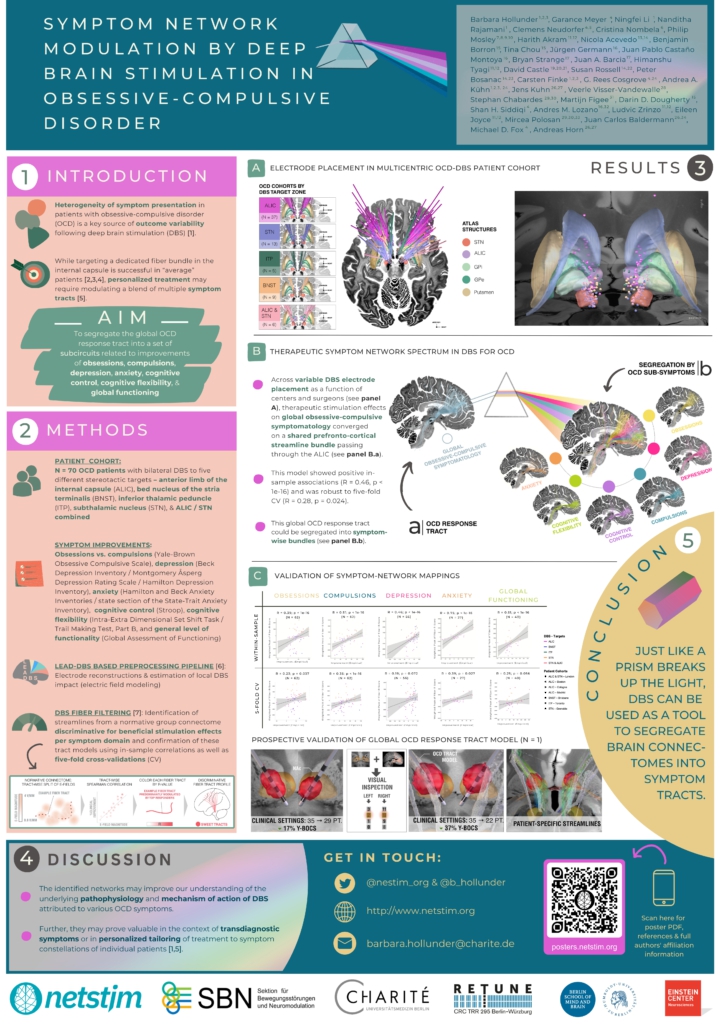
Neudorfer*, Mustin* et al. (3rd DBS Expert Summit 2026)
Translating the Transcriptome: A Connectomics Approach for Gene-Network Mapping and Clinical Application
Affiliations
1Department of Neurosurgery, Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA.
2Center for Brain Circuit Therapeutics Department of Neurology Brigham & Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA.
3Movement Disorders and Neuromodulation Unit, Department of Neurology, Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, corporate member of Freie Universität Berlin and Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Berlin, Germany.
4Einstein Center for Neurosciences Berlin, Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Berlin, Germany.
5Berlin School of Mind and Brain, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Berlin, Germany.
6Department of Neurology, Tufts Medical Center, Boston, MA, USA.
7Clinical Brain Networks Group, QIMR Berghofer Medical Research Institute, Herston, Brisbane, Queensland, Australia.
8Neurosciences Queensland, St. Andrew’s War Memorial Hospital, Spring Hill, Queensland, Australia.
9Queensland Brain Institute, University of Queensland, St. Lucia, Brisbane, Queensland, Australia.
10Australian e-Health Research Centre, Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation Health and Biosecurity, Herston, Queensland, Australia.
11Department of Clinical and Movement Neurosciences, University College London Queen Square Institute of Neurology, London, United Kingdom.
12National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery, University College London Queen Square Institute of Neurology, London, United Kingdom.
13Centre for Mental Health, Swinburne University of Melbourne, Victoria, Australia.
14St. Vincent’s Hospital, Melbourne, Victoria, Australia.
15Department of Psychiatry, University of Melbourne, Melbourne, Australia.
16Movement Disorders and Neuromodulation Centre, Department of Neurology, University of California, San Francisco, San Francisco, CA, USA.
17Department of Neurological Surgery, University of California, San Francisco, San Francisco, CA, USA.
18Department of Neurology, Amsterdam University Medical Center, Amsterdam, Netherlands.
19Department of Neurosurgery, Hospital Clínico San Carlos, Instituto de Investigacion Sanitaria San Carlos, Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Madrid, Spain.
20Department of Neurosurgery, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX, USA.
21Menninger Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX, USA.
22Department of Stereotactic and Functional Neurosurgery, Faculty of Medicine and University Hospital Cologne, University of Cologne, Cologne, Germany.
23Nash Family Center for Advanced Circuit Therapeutics, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, New York.
24Department of Neuroscience, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, New York.
25Department of Psychiatry, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, New York.
26Department of Psychiatry, Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, USA.
27Cognitive Neuroscience Unit, School of Psychology, Deakin University, Geelong, VIC, Australia.
28Turku Brain and Mind Center, University of Turku, Turku, Finland.
29Department of Neurosurgery, Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Berlin, Germany.
30Cluster of Excellence Matters of Activity. Image Space Material, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Berlin, Germany.
31Department of Neurology, Toronto Western Hospital, Toronto, Canada.
32Psychiatric and Neurodevelopmental Genetics Unit, Center for Genomic Medicine, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA, USA.
33Center for Genomic Medicine, Department of Medicine, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA, USA.
34Department of Psychiatry, Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA.
35Institute of Neurogenetics, University of Lubeck, Lubeck, Germany.
Goede et al. (3rd DBS Expert Summit 2026)
Action vs. rest tremor map to different networks within primary motor cortex
Affiliations
- Department of Neurology with Experimental Neurology, Movement Disorders and Neuromodulation Unit, Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, corporate member of Freie Universität Berlin and Humboldt- Universität zu Berlin, Berlin, Germany
- Center for Brain Circuit Therapeutics, Department of Neurology, Brigham & Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA
- Einstein Center for Neurosciences Berlin, Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, corporate member of Freie Universität Berlin and Humboldt- Universität zu Berlin, Berlin, Germany
- Institute for Network Stimulation, Department of Stereotactic and Functional Neurosurgery, University Hospital Cologne, Germany
- Department of Neurosurgery, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing, 100853, China
- Department of Neurosurgery, Hainan Hospital of Chinese PLA General Hospital, Sanya, Hainan, 572000, China
- Department of Neurosurgery, The National Key Clinic Specialty, Shenzhen Key Laboratory of Neurosurgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Shenzhen University, Shenzhen Second
- Department of Neurology, University Hospital Würzburg, Würzburg, Germany
- MGH Neurosurgery & Center for Neurotechnology and Neurorecovery (CNTR) at MGH Neurology Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA
References:
- Goede, L.L., Al-Fatly, B., Li, N., Sobesky, L.K., Bahners, B.H., Zvarova, P., Neudorfer, C., Reich, M., Volkmann, J., Zhang, C., et al. (2025). Convergent mapping of a tremor treatment network. Nat Commun 16, 4772. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-60089-6.
- Penfield, W., and Boldrey, E. (1937). Somatic motor and sensory representation in the cerebral cortex of man as studied by electrical stimulation. Brain 60, 389–443. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/60.4.389.
- Vogt, C., and Vogt, O. (1926). Die vergleichend-architektonische und die vergleichend-reizphysiologische Felderung der Großhirnrinde unter besonderer Berücksichtigung der menschlichen. Naturwissenschaften 14, 1190–1194. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01451766.
- Gordon, E.M., Chauvin, R.J., Van, A.N., Rajesh, A., Nielsen, A., Newbold, D.J., Lynch, C.J., Seider, N.A., Krimmel, S.R., Scheidter, K.M., et al. (2023). A somato-cognitive action network alternates with effector regions in motor cortex. Nature 617, 351–359. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-023-05964-2.
- Dosenbach, N.U.F., Raichle, M.E., and Gordon, E.M. (2025). The brain’s action-mode network. Rev. Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41583-024-00895-x.
- Neudorfer, C., Butenko, K., Oxenford, S., Rajamani, N., Achtzehn, J., Goede, L., Hollunder, B., Ríos, A.S., Hart, L., Tasserie, J., et al. (2023). Lead-DBS v3.0: Mapping deep brain stimulation effects to local anatomy and global networks. NeuroImage 268, 119862. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2023.119862.
Sahin et al. (3rd DBS Expert Summit 2026)
Deep Brain Stimulation for Tourette Syndrome: from voxels to networks
Affiliations
- Einstein Center for Neurosciences Berlin, Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Berlin 10117, Germany
- Institute for Network Stimulation, Department of Stereotactic and Functional Neurosurgery, University Hospital Cologne, Cologne, Germany
- Movement Disorders and Neuromodulation Unit, Department of Neurology with Experimental Neurology, Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Corporate Member of Freie Universität Berlin and Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Berlin 10117, Germany
- Department of Neurology, Norman Fixel Institute for Neurological Diseases, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL, USA; Department of Neurology, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL, USA.
- Center for Brain Circuit Therapeutics, Department of Neurology, Mass General Brigham, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA
- Julius-Maximilian-University Wuerzburg, Germany
- Northwestern Polytechnical University, China
- Department of Neurosurgery, Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA
- Institute of Neuroradiology, Charité-Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Corporate Member of Freie Universität Berlin, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, and Berlin Institute of Health (BIH), Berlin, Germany.
- Department of Psychiatry and Psychotherapy, Medical Center – University of Freiburg, Faculty of Medicine, University of Freiburg, Freiburg, Germany.
- University of Cologne, Faculty of Medicine and University Hospital Cologne, Department of Neurology, Cologne, Germany
- Department of Psychiatry and Psychotherapy, Faculty of Medicine and University Hospital Cologne, University of Cologne, Cologne, Germany
- Alexianer Hospital Cologne, Alexianer Köln GmbH, Cologne, Germany
- Department of Psychiatry and Psychotherapy III, LVR Klinik Bonn, Bonn 53111, Germany.
- Department of Stereo tactic and Functional Neurosurgery, Faculty of Medicine and University Hospital Cologne, University of Cologne, Cologne, Germany
- Sorbonne University, Inserm U1127, CNRS UMR7225, UM75, Paris Brain Institute, Movement Investigation and Therapeutics Team, 75013 Paris, France.
- Department of Clinical Neurophysiology, Hopital Saint Antoine, 75012 Paris, France
- Sorbonne University, Paris Brain Institute – ICM, Inserm, CNRS, Department of Radiology, Hôpital de la Pitié Salpêtrière (DMU 6), AP-HP, 75013, Paris, France.
- Inserm 1127, Sorbonne Université, UPMC Univ Paris 06, UMRS 1127, CNRS, UMR 7225, Paris Brain Institute, Paris, France.
- Department of Neurophysiology, CHU Rouen, Rouen University, 76000 Rouen, France
- Department of Neurosurgery, Maastricht University Medical Centre, 6229 HX Maastricht, The Netherlands
- Department of Neurosurgery, Zuyderland Medical Center, Academic Neurosurgical Center Limburg, Heerlen, The Netherlands
- Department of Psychiatry, Maastricht University Medical Centre, 6229 HX Maastricht, The Netherlands
- Department of Neurosurgery, Rujin Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China
- Beijing Neurosurgical Institute, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China.
- Department of Neurosurgery, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing, 100853, China
- Department of Neurosurgery, Hainan Hospital of Chinese PLA General Hospital, Sanya, Hainan, 572000, China
- Neurosurgical Department, IRCCS Istituto Ortopedico Galeazzi, Milan, Lombardia, Italy
- Tourette’s Syndrome and Movement Disorders Center, IRCCS Istituto Ortopedico Galeazzi, Milan, Lombardia, Italy
- Center for Neuromodulation, Departments of Neurology and Neurosurgery, New York University Medical Center, New York, New York, USA
- Department of Neurology, University of California San Francisco, San Francisco, California, USA
- Department of Clinical and Movement Neurosciences, UCL Queen Square Institute of Neurology, London, UK
- National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery, UCL Queen Square Institute of Neurology, London, UK
- Department of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine, Maastricht University Medical Center, the Netherlands
- Mental Health and Neuroscience Research Institute, Maastricht University, the Netherlands
- Parkinson and Movement Disorders Unit, Fondazione IRCCS Istituto Neurologico Carlo Besta, Milan, Italy
- The BioRobotics Institute, Scuola Superiore Sant’Anna, Pisa, Italy
- Department of Excellence in Robotics and AI, Scuola Superiore Sant’Anna, Pisa, Italy
- Division of Neurosurgery, Department of Surgery, Medical School, Federal University of Goiás, Goiânia, Brazil.
- Division of Neurosurgery, Department of Surgery, University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario, Canada.
- Krembil Research Institute, Toronto, Ontario, Canada.
- CERVO Brain Research Centre, Quebec City, Quebec, Canada
- Department of Neurology and Neurosurgery, Montreal Neurological Institute, McGill University Health Centre, McGill University, Montreal, QC, Canada.
- Department of Neurosurgery, Shands at University of Florida, University of Florida, Gainesville.
- Department of Neurosurgery, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL, USA; J Crayton Pruitt Family Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL, USA.
Backdrops & 3D Atlas Structures:
- Friedrich H, Sahin IA, Rajamani N, et al. A precise atlas of the human subcortex. bioRxiv. Preprint posted online February 15, 2026:2026.02.13.705755. doi:10.64898/2026.02.13.705755
- Amunts K, Lepage C, Borgeat L, et al. BigBrain: An Ultrahigh-Resolution 3D Human Brain Model. Science. 2013;340(6139):1472-1475. doi:10.1126/science.1235381
- Edlow BL, Mareyam A, Horn A, et al. 7 Tesla MRI of the ex vivo human brain at 100 micron resolution. Sci Data. 2019;6(1):244. doi:10.1038/s41597-019-0254-8
Zvarova et al. (3rd DBS Expert Summit 2026)
Imaging-Informed Guidance for Subthalamic DBS: Translating Group Models to Individual Contacts
Affiliations
1Movement Disorder and Neuromodulation Unit, Department of Neurology, Charité-Universitätsmedizin Berlin, corporate member of Freie Universität Berlin and Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Berlin, Germany
2Einstein Center for Neurosciences Berlin, Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Berlin, Germany
3Center for Brain Circuit Therapeutics, Department of Neurology, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston MA 02115, USA
4Network Stimulation Institute, Department of Stereotactic and Functional Neurosurgery, University Hospital Cologne, Germany
5Department of Neurology, Faculty of Medicine and University Hospital Cologne, University of Cologne, Cologne, Germany
6Department of Neurology, Center for Movement Disorders and Neuromodulation, Medical Faculty and University Hospital Düsseldorf, Heinrich Heine University Düsseldorf
7Institute of Clinical Neuroscience and Medical Psychology, Medical Faculty and University Hospital Düsseldorf, Heinrich Heine University Düsseldorf
8Berlin School of Mind and Brain, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Berlin, Germany
9Brigham & Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Department of Psychiatry
10Department of Neurology, University Clinic of Würzburg, Josef-Schneider-Str. 11, 97080, Würzburg, Germany
11Department of Neurology, Amsterdam University Medical Center, University of Amsterdam, Amsterdam, The Netherlands
12Department of Neurosurgery, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing, 100853, China
13Department of Neurosurgery, Hainan Hospital of Chinese PLA General Hospital, Sanya, Hainan, 572000, China
14Department of Neurosurgery, The National Key Clinic Specialty, Shenzhen Key Laboratory of Neurosurgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Shenzhen University, Shenzhen Second People’s Hospital, Shenzhen, 518035, China
15Bernstein Center for Computational Neuroscience Berlin, Berlin, Germany
16NeuroCure Clinical Research Centre, Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, corporate member of Freie Universität Berlin and Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Berlin, Germany
17Clinical Neurotechnology Laboratory, Department of Psychiatry and Neurosciences
(CCM), Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Berlin, Germany
18Berlin Center for Advanced Neuroimaging (BCAN), Charité— Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Berlin, Germany
19Hertie Institute for AI in Brain Health, University of Tübingen, Germany
20Department of Stereotactic and Functional Neurosurgery, Faculty of Medicine and University Hospital Cologne, University of Cologne, Cologne, Germany
21MGH Neurosurgery & Center for Neurotechnology and Neurorecovery (CNTR) at MGH Neurology Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA 02114, USA
References
[1-4]
Richards M, Marder K, Cote L, Mayeux R. Interrater reliability of the unified Parkinson’s disease rating scale motor examination. Movement Disorders. 1994;9(1):89-91. doi:10.1002/mds.870090114
Bennett DA, Shannon KM, Beckett LA, Goetz CG, Wilson RS. Metric properties of nurses’ ratings of parkinsonian signs with a modified Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale. Neurology. 1997;49(6):1580-1587. doi:10.1212/WNL.49.6.1580
Siderowf A, McDermott M, Kieburtz K, et al. Test-Retest reliability of the Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale in patients with early Parkinson’s disease: Results from a multicenter clinical trial. Mov Disord. 2002;17(4):758-763. doi:10.1002/mds.10011
Metman LV, Myre B, Verwey N, et al. Test-retest reliability of UPDRS-III, dyskinesia scales, and timed motor tests in patients with advanced Parkinson’s disease: An argument against multiple baseline assessments. Mov Disord. 2004;19(9):1079-1084. doi:10.1002/mds.20101
[5]
Cavallieri F, Fraix V, Bove F, et al. Predictors of Long-Term Outcome of Subthalamic Stimulation in Parkinson Disease. Annals of Neurology. 2020;89(3):587-597. doi:10.1002/ana.25994
[6-8]
Maks CB, Butson CR, Walter BL, Vitek JL, McIntyre CC. Deep brain stimulation activation volumes and their association with neurophysiological mapping and therapeutic outcomes. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2009;80(6):659-666. doi:10.1136/jnnp.2007.126219
Noecker AM, Frankemolle-Gilbert AM, Howell B, et al. StimVision v2: Examples and Applications in Subthalamic Deep Brain Stimulation for Parkinson’s Disease. Neuromodulation. 2021;24(2):248-258. doi:10.1111/ner.13350
Rajamani N, Friedrich H, Butenko K, et al. Deep brain stimulation of symptom-specific networks in Parkinson’s disease. Nat Commun. 2024;15(1):4662. doi:10.1038/s41467-024-48731-1
[9]
Alonso F, Zsigmond P, Wårdell K. Influence of Virchow-Robin spaces on the electric field distribution in subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation. Clinical Neurology and Neurosurgery. 2021;204:106596. doi:10.1016/j.clineuro.2021.106596
[10]
Muthuraman M, Deuschl G, Koirala N, Riedel C, Volkmann J, Groppa S. Effects of DBS in parkinsonian patients depend on the structural integrity of frontal cortex. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):43571. doi:10.1038/srep43571
[11]
Soulas T, Sultan S, Gurruchaga JM, Palfi S, Fénelon G. Depression and Coping as Predictors of Change After Deep Brain Stimulation in Parkinson’s Disease. World Neurosurgery. 2011;75(3):525-532. doi:10.1016/j.wneu.2010.06.015
Meyer et al. (NYC Neuromodulation 2024)
Deep Brain Stimulation sites causing or improving psychosis
Affiliations
GM Meyer, AR Pines, FLWVJ Schaper, C Neudorfer, SH Siddiqi, A Horn: Center for Brain Circuit Therapeutics, Department of Neurology, Brigham & Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA
Roldan A, Aracil-Bolanos I, JA Aibar-Durán, I Corripio: Institut d’Investigacio Biomedica-Sant Pau (IIB-SANT PAU), Hospital de la Santa Creu i Sant Pau, Barcelona, Spain
Roldan A: Spanish National Network for Research in Mental Health (CIBERSAM), Madrid, Spain
C Neudorfer, DD Dougherty, A Horn: Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA, USA
S Järvenpää, K Lehtimäki, J Peltola: Tampere University Hospital and University of Tampere, Faculty of Medicine and Health Technology, Tampere, Finland
H Kamo, G Oyama, N Hattori: School of Medicine, Juntendo University, Tokyo, Japan
S Piacentini, LM Romito: Fondazione IRCCS Istituto Neurologico Carlo Besta, Milano, Italy
PE Mosley: QIMR Berghofer Medical Research Institute, Queensland Brain Institute and CSIRO; Neurosciences Queensland, St Andrew’s War Memorial Hospital; Queensland Brain Institute, University of Queensland, St Lucia; Australian eHealth Research Centre, CSIRO Health and Biosecurity, Queensland, Australia
AS Widge: Department of Psychiatry, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN, USA
Y Temel, RPW Rouhl: Department of Neurology, Maastricht University Medical Center and School for Mental Health and Neuroscience, Maastricht University, Maastricht, Netherlands
RPW Rouhl, A Colon: Academic Center for Epileptology Kempenhaeghe/MUMC+, Heeze and Maastricht, Netherlands
A Colon: Centre d’Etudes et Traitement d’Epilepsie (CETE), CHU Martinique, France
M Maarouf: Division of Stereotaxis and Functional Neurosurgery, University of Cologne, Cologne, Germany
A Macerollo, J Osman Farah: The Walton Centre NHS Foundation Trust for Neurology and Neurosurgery, Liverpool, UK
A Macerollo: Institute of Systems, Molecular and Integrative Biology, University of Liverpool, Liverpool, UK; Department of Psychology, Manchester Metropolitan University, Manchester, UK
H Akram, T Foltynie: University College London Queen Square Institute of Neurology, London, UK
CC Zhang: Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shangai, China
I Corripio: Vic University Hospital, Barcelona, Spain
A Horn: Department of Neurology,and Einstein Center for Neurosciences, Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Berlin, Germany; Berlin School of Mind and Brain, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Berlin, Germany
References
Psychosis with dislodged GPi electrode
#1 – Piacentini, S. et al. Mov Disord 23, 147–150 (2008).
Psychosis with NAc-DBS
Graat, I. et al. Brain Stimul 12, 770–771 (2019).
#2 – Testo, A. A. et al. Brain Stimul 13, 1317–1319 (2020).
Psychosis and suicidality with GPi-DBS
#3 – Hanna, S., Palmadottir, V., Penar, P. L. & Boyd, J. T. Clin Park Relat Disord 8, 100175 (2022).
Psychosis with ANT-DBS
#8-9 – Järvenpää, S. et al. Epilepsy Behav 88, 373–379 (2018).
#10 – Schaper, F. L. W. V. J. et al. Neurosurgery 87, 602–610 (2020).
#11 – Olaciregui Dague, K., Witt, J.-A., von Wrede, R., Helmstaedter, C. & Surges, R. Frontiers in Neurology 14, (2023).
#12 – Costa-Gertrudes, R. et al. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 100, 108–120 (2022).
Psychosis with STN-DBS
#4 – Mosley, P. E., Marsh, R., Perry, A., Coyne, T. & Silburn, P. JNP 30, 246–249 (2018).
#5 – Neudorfer, C. et al. Neuromodulation 22, 493–502 (2019).
#6 -Ito, M. et al. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 74, 328–329 (2020).
#7 -Macerollo, A. et al. Neurol Sci 41, 2639–2640 (2020).
Raucher-Chéné, D., Charrel, C.-L., Maindreville, A. D. de & Limosin, F. Journal of the Neurological Sciences 273, 116–117 (2008).
Herzog, J. et al. Mov Disord 18, 1382–1384 (2003).
Kulisevsky, J. et al. Neurology 59, 1421–1424 (2002).
Clinical trials of DBS for schizophrenia
#13-20 – Corripio, I. et al. EBioMedicine 51, 102568 (2020).
#21 – Cascella, N. et al. Biol Psychiatry 90, e57–e59 (2021).
#22-23 – Wang, Y. et al. Neurosurg Focus 49, E9 (2020).
Zhou, B. et al. Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci 18, 636–640 (2020).
NBM-DBS improving hallucinations
#24-25 – Gratwicke, J. et al. JAMA Neurol 75, 169–178 (2018).
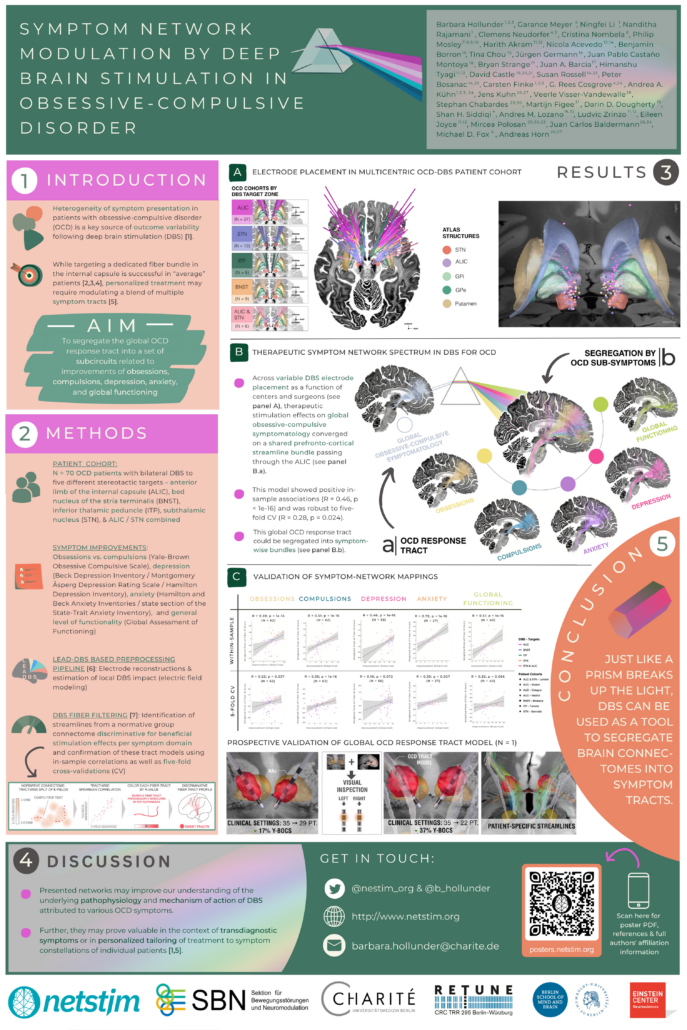
Hollunder et al. (OHBM 2024)
Symptom Network Modulation of Deep Brain Stimulation in Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
Affiliations
- Department of Neurology, Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Berlin, Germany
- Einstein Center for Neurosciences Berlin, Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Berlin, Germany
- Berlin School of Mind and Brain, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Berlin, Germany
- Center for Brain Circuit Therapeutics, Department of Neurology, Brigham & Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA
- Department of Neurosurgery, Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA
- Biological and Health Psychology, School of Psychology, Universidad Autónoma de Madrid, Spain
- Clinical Brain Networks Group, QIMR Berghofer Medical Research Institute, Herston, Queensland, Australia
- Neurosciences Queensland, St Andrew’s War Memorial Hospital, Spring Hill, Queensland, Australia
- Queensland Brain Institute, University of Queensland, St Lucia, Queensland, Australia
- Australian eHealth Research Centre, CSIRO Health and Biosecurity, Herston, Queensland, Australia
- Department of Clinical and Movement Neurosciences, UCL Queen Square Institute of Neurology, London, UK
- National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery, UCL Queen Square Institute of Neurology, London, UK
- Centre for Mental Health, Swinburne University of Technology, Melbourne, VIC, Australia
- Vincent’s Hospital Melbourne, Melbourne, Australia
- Department of Psychiatry, Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA
- Division of Neurosurgery, Department of Surgery, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada
- Department of Neurosurgery, Hospital Clinico San Carlos, Instituto de Investigacion Sanitaria San Carlos, Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Madrid, Spain
- Laboratory for Clinical Neuroscience, Center for Biomedical Technology, Universidad Politécnica de Madrid, IdISSC, Madrid, Spain
- Centre for Complex Interventions, Centre for Addiction and Mental Health, Toronto, ON, Canada
- Institute of Medical Sciences, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada
- Department of Psychiatry, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada
- Centre for Mental Health, Swinburne University, Melbourne, Australia
- Department of Psychiatry, University of Melbourne, Melbourne, Australia
- Department of Neurosurgery, Brigham & Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA
- NeuroCure Cluster of Excellence, Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Berlin, Germany
- Department of Psychiatry and Psychotherapy, Faculty of Medicine and University Hospital Cologne, University of Cologne, Cologne, Germany
- Johanniter Hospital Oberhausen, EVKLN, Department of Psychiatry, Psychotherapy and Psychosomatics, Oberhausen, Germany
- Department of Stereotactic and Functional Neurosurgery, Faculty of Medicine and University Hospital Cologne, University of Cologne, Cologne, Germany
- Univ Grenoble Alpes, Grenoble, France
- Inserm, U1216, Grenoble Institut des Neurosciences, Grenoble, France
- Department of Psychiatry, Icahn School of Medicine, Mount Sinai Hospital, New York, USA
- Krembil Brain Institute, Toronto, ON, Canada
- Psychiatry Department, CHU Grenoble Alpes, Grenoble, France
- Department of Neurology, Faculty of Medicine and University Hospital Cologne, University of Cologne, Cologne, Germany
References
[1] Figee, M., & Mayberg, H. (2021). The future of personalized brain stimulation. Nature Medicine, 27, 196–197. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-021-01243-7
[2] Baldermann, J. C. et al. (2019). Connectivity profile predictive of effective deep brain stimulation in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Biological Psychiatry, 85(9), 735–743. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2018.12.019
[3] Baldermann, J. C. et al. (2021). Connectomic deep brain stimulation for obsessive-compulsive disorder. Biological Psychiatry, 90(10), 678–688. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2021.07.010
[4] Li, N. et al. (2020). A unified connectomic target for deep brain stimulation in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Nature Communications, 11, 3364. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-16734-3
[5] Hollunder, B. et al. (2022). Toward personalized medicine in connectomic deep brain stimulation. Progress in Neurobiology, 210(210), 102211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2021.102211
[6] Neudorfer, C. et al. Lead-DBS v3.0: Mapping deep brain stimulation effects to local anatomy and global networks. Neuroimage 268, 119862 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2023.119862
[7] Irmen, F. et al. (2020). Left prefrontal connectivity links subthalamic stimulation with depressive symptoms. Annals of Neurology, 87(6), 962–975. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.25734
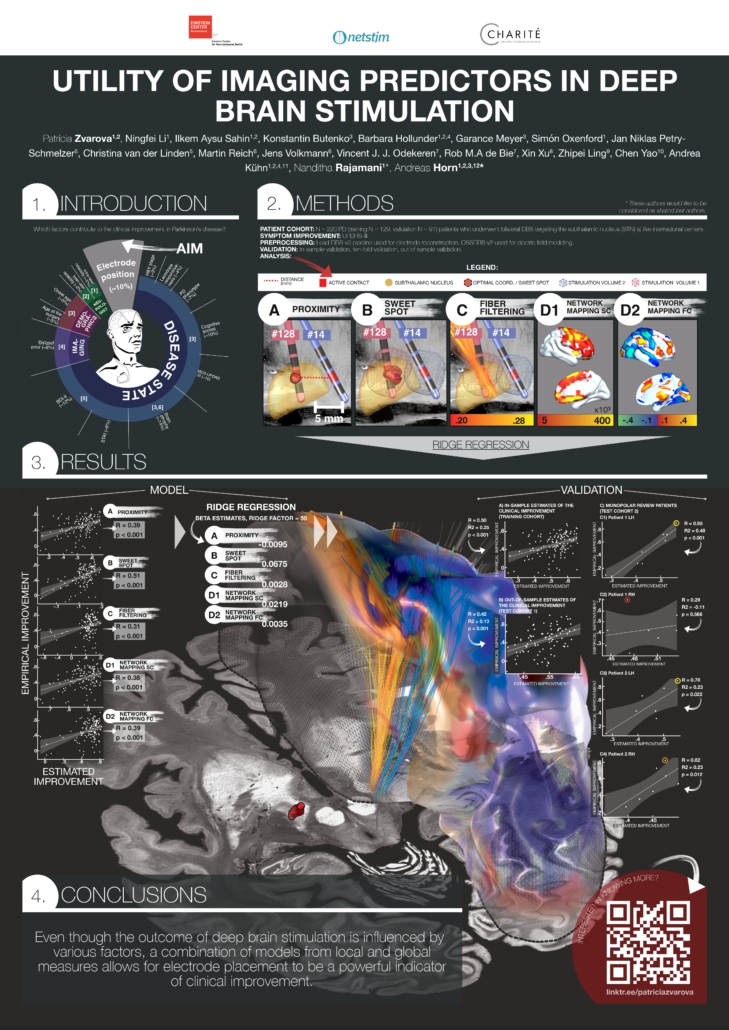
Zvarova et al. 2024
Utility of Imaging Predictors in Deep Brain Stimulation
AFFILIATIONS:
Patricia Zvarova1,2, Ningfei Li1, Ilkem Aysu Sahin1,2, Konstantin Butenko3, Barbara Hollunder1,2,4, Garance Meyer3, Simón Oxenford1, Jan Niklas Petry-Schmelzer5, Christina van der Linden5, Martin Reich6, Jens Volkmann6, Vincent J. J. Odekeren7, Rob M.A de Bie7, Xin Xu8, Zhipei Ling9, Chen Yao10, Andrea Kühn1,2,4,11, Nanditha Rajamani1*, Andreas Horn1,2,3,12*
- Movement Disorders and Neuromodulation Unit, Department of Neurology, Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Berlin, Germany
- Einstein Center for Neurosciences Berlin, Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Berlin, Germany
- Center for Brain Circuit Therapeutics, Department of Neurology, Brigham & Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA
- Berlin School of Mind and Brain, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Berlin, Germany
- University of Cologne, Faculty of Medicine and University Hospital Cologne, Department of Neurology, Cologne, Germany
- Department of Neurology, University Clinic of Würzburg, Josef-Schneider-Str. 11, 97080 Würzburg, Germany
- Department of Neurology, Amsterdam University Medical Center, Amsterdam, The Netherlands
- Department of Neurosurgery, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100853, China
- Department of Neurosurgery, Hainan Hospital of Chinese PLA General Hospital, Sanya, Hainan 572000, China
- Department of Neurosurgery, The National Key Clinic Specialty, Shenzhen Key Laboratory of Neurosurgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Shenzhen University, Shenzhen Second People’s Hospital, Shenzhen 518035, China
- NeuroCure Cluster of Excellence, Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Berlin, Germany
- Center for Brain Circuit Therapeutics, Brigham & Women’s Hospital, Boston, MA, USA
References:
- Metman, L.V. et al. (2004) ‘Test-retest reliability of UPDRS-III, dyskinesia scales, and timed motor tests in patients with advanced Parkinson’s disease: An argument against multiple baseline assessments’, Movement Disorders, 19(9), pp. 1079– Available at: https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.20101.
- Bennett, D.A. et al. (1997) ‘Metric properties of nurses’ ratings of parkinsonian signs with a modified Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale’, Neurology, 49(6), pp. 1580– Available at: https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.49.6.1580.; Siderowf, A. et al. (2002) ‘Test-Retest reliability of the Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale in patients with early Parkinson’s disease: Results from a multicenter clinical trial’, Movement Disorders, 17(4), pp. 758–763. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.10011.; Richards, M. et al. (1994) ‘Interrater reliability of the unified Parkinson’s disease rating scale motor examination’, Movement Disorders, 9(1), pp. 89–91. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.870090114.
- Cavallieri, F. et al. (2020) ‘Predictors of Long-Term Outcome of Subthalamic Stimulation in Parkinson Disease’, Annals of Neurology, 89(3), pp. 587– Available at: https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.25994.
- Soulas, T. et al. (2011) ‘Depression and Coping as Predictors of Change After Deep Brain Stimulation in Parkinson’s Disease’, World Neurosurgery, 75(3), pp. 525– Available at: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2010.06.015.
- Muthuraman, M. et al. (2017) ‘Effects of DBS in parkinsonian patients depend on the structural integrity of frontal cortex’, Scientific Reports, 7(1), p. 43571. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1038/srep43571
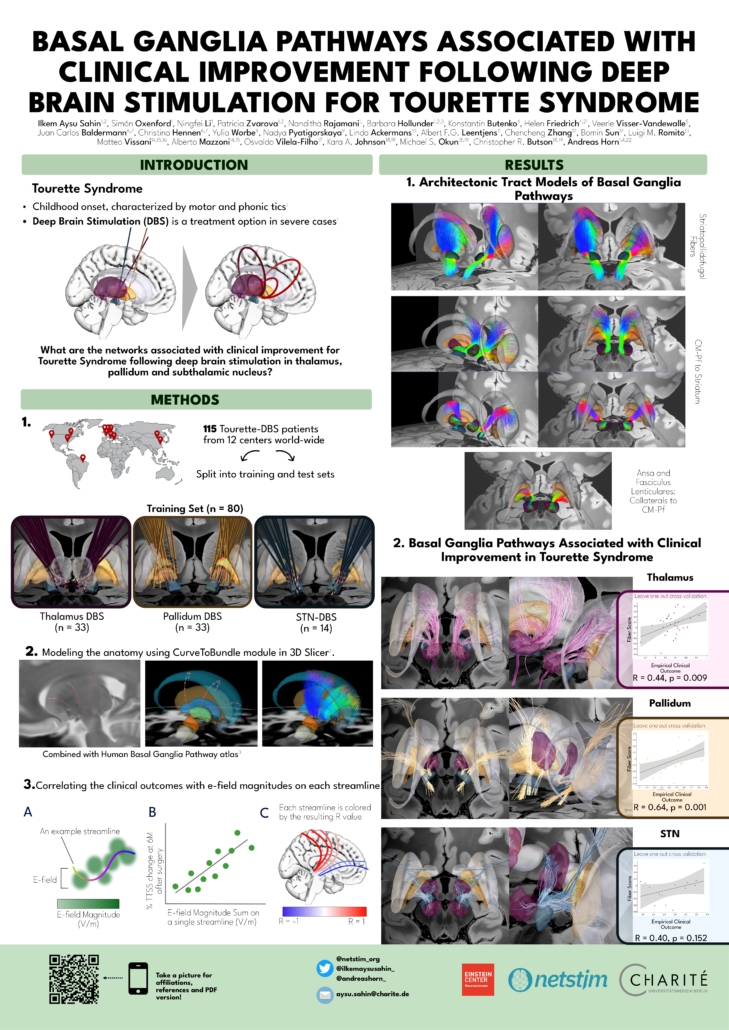
Sahin et al. 2024
Basal Ganglia Pathways Associated with Clinical Improvement Following Deep Brain Stimulation For Tourette Syndrome
Author(s): Ilkem Aysu Sahin1,2, Simón Oxenford1, Ningfei Li1, Patricia Zvarova1,2, Nanditha Rajamani1, Barbara Hollunder1,2,3, Konstantin Butenko4, Helen Friedrich4,21, Veerle Visser-Vandewalle5, Juan Carlos Baldermann6,7, Christina Hennen6,7, Yulia Worbe8, Nadya Pyatigorskaya9, Linda Ackermans10, Albert F.G. Leentjens11, Chencheng Zhang12, Bomin Sun12, Luigi M. Romito13, Matteo Vissani14,15,16, Alberto Mazzoni14,15, Osvaldo Vilela-Filho17, Kara A. Johnson18,19, Michael S. Okun18,19, Christopher R. Butson18,20, Andreas Horn1, 4, 22
Affiliations
- Movement Disorder and Neuromodulation Unit, Department of Neurology, Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, corporate member of Freie Universität Berlin and Humboldt- Universität zu Berlin, 10117 Berlin, Germany
- Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Einstein Center for Neurosciences Berlin, 10117, Berlin, Germany
- Berlin School of Mind and Brain, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Berlin, Germany
- Center for Brain Circuit Therapeutics Department of Neurology Brigham & Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston MA 02115, USA
- Department of Stereotactic and Functional Neurosurgery, University Hospital of Cologne, Cologne, Germany.
- University of Cologne, Faculty of Medicine and University Hospital Cologne, Department of Psychiatry and Psychotherapy, Cologne, Germany
- University of Cologne, Faculty of Medicine and University Hospital Cologne, Department of Neurology, Cologne, Germany
- Sorbonne University, ICM, Inserm, CNRS, Department of Neurophysiology, Hôpital Saint Antoine (DMU 6), AP-HP, 75013 Paris, France
- Sorbonne University, Paris Brain Institute – ICM, Inserm, CNRS, Department of Radiology, Hôpital de la Pitié Salpêtrière (DMU 6), AP-HP, 75013, Paris, France.
- Department of Neurosurgery, Maastricht University Medical Centre, 6229 HX Maastricht, The Netherlands
- Department of Psychiatry, Maastricht University Medical Centre, 6229 HX Maastricht, The Netherlands
- Department of Neurosurgery, Rujin Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China
- Parkinson and Movement Disorders Unit, Fondazione IRCCS Istituto Neurologico Carlo Besta, Milan, Italy
- The BioRobotics Institute, Scuola Superiore Sant’Anna, Pisa, Italy
- Department of Excellence in Robotics and AI, Scuola Superiore Sant’Anna, Pisa, Italy
- Department of Neurosurgery, Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA
- Division of Neurosurgery, Department of Surgery, Medical School, Federal University of Goiás, Goiânia, Brazil.
- Norman Fixel Institute for Neurological Diseases, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL, USA.
- Department of Neurology, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL, USA.
- Scientific Computing and Imaging Institute Department of Bioengineering, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, UT, USA.
- University of Würzburg, Faculty of Medicine, Josef-Schneider-Str. 2, 97080, Würzburg, Germany
- MGH Neurosurgery & Center for Neurotechnology and Neurorecovery (CNTR) at MGH Neurology Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA 02114, USA
References
- Johnson KA, Worbe Y, Foote KD, Butson CR, Gunduz A, Okun MS. Tourette syndrome: clinical features, pathophysiology, and treatment. Lancet Neurol. 2023;22(2):147-158. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(22)00303-9
- Fedorov A, Beichel R, Kalpathy-Cramer J, et al. 3D Slicer as an image computing platform for the Quantitative Imaging Network. Magn Reson Imaging. 2012;30(9):1323-1341. doi:10.1016/j.mri.2012.05.001. http://www.slicer.org
- Petersen MV, Mlakar J, Haber SN, et al. Holographic Reconstruction of Axonal Pathways in the Human Brain. Neuron. 2019;104(6):1056-1064.e3. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2019.09.030
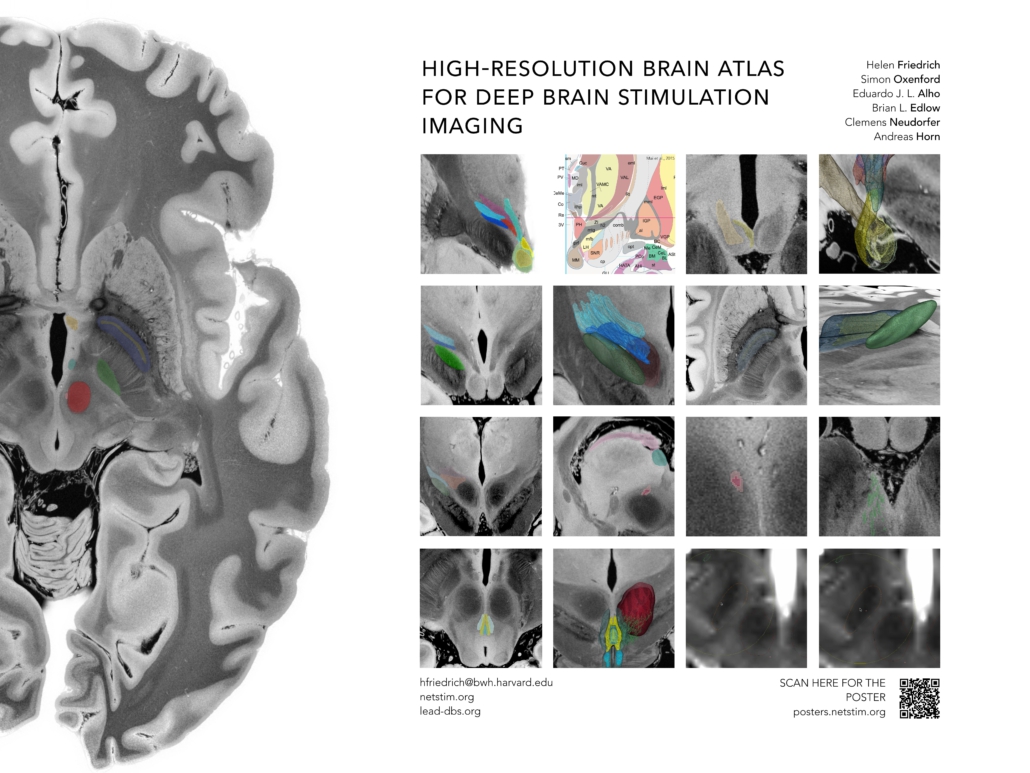
Friedrich et al. 2023
High-resolution brain atlas for deep brain stimulation imaging
Mesoscale Brain Mapping Symposium 2023 | Poster Abstract
A High Resolution Brain Atlas for Deep Brain Stimulation Imaging
Helen Friedrich1,2, Simon Oxenford3, Eduardo J. L. Alho4, Brian L. Edlow5,6, Clemens Neudorfer1,3,7, Andreas Horn1,3,5,7
Contact: hfriedrich@bwh.harvard.edu; ahorn1@bwh.harvard.edu
1 Center for Brain Circuit Therapeutics Department of Neurology Brigham & Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston MA 02115, USA
2 Julius-Maximilian-University Wuerzburg, Germany
3 Movement Disorder and Neuromodulation Unit, Department of Neurology, Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, corporate member of Freie Universität Berlin and Humboldt- Universität zu Berlin, Department of Neurology, 10117 Berlin, Germany
4 Clinic of Pain and Functional Neurosurgery, São Paulo, Brazil
5 Center for Neurotechnology and Neurorecovery, Department of Neurology, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA 02114, USA
6 Athinoula A. Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging, Massachusetts General Hospital, Charlestown, MA, USA
7 Brain Modulation Lab, Department of Neurosurgery, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA, 02114, USA
Background
The success of deep brain stimulation therapy is defined by the exact placement of electrodes in relation to their targets. Overlaps between stimulation volumes and anatomical structures may account for clinical outcomes. To investigate this, precise definitions of anatomical structures are critical. These target structures frequently comprise anatomical structures or tracts that are often not discernable on conventional neuroimaging.
Methods
We aimed to create a high-resolution atlas including both grey and white matter based on a 100-micron ex-vivo MRI brain scan (Edlow et al., 2019). Histological data, postmortem fiber dissections, and expert opinions of clinicians and anatomists were used to inform and enrich anatomical validity. Segmentations of gray- (n=15) and white- (n=16) matter structures at the level of the subthalamus were carried out on the high resolution MRI scan and converted into MNI ICBM 2009b NLIN ASYM space. This spatial transform from MRI native to template space was carried out using a manually curated warpfield that accounts for proper definitions of target structures in standard space.
Results & Conclusions
The main result of this work should be seen in a high-resolution atlas of the human subthalamus comprising a total of 31 gray and white matter regions per hemisphere. Together with the ex-vivo MRI template and a precise manual registration to MNI space, this dataset is deformable to patient MRIs and can be readily applied in DBS imaging studies.
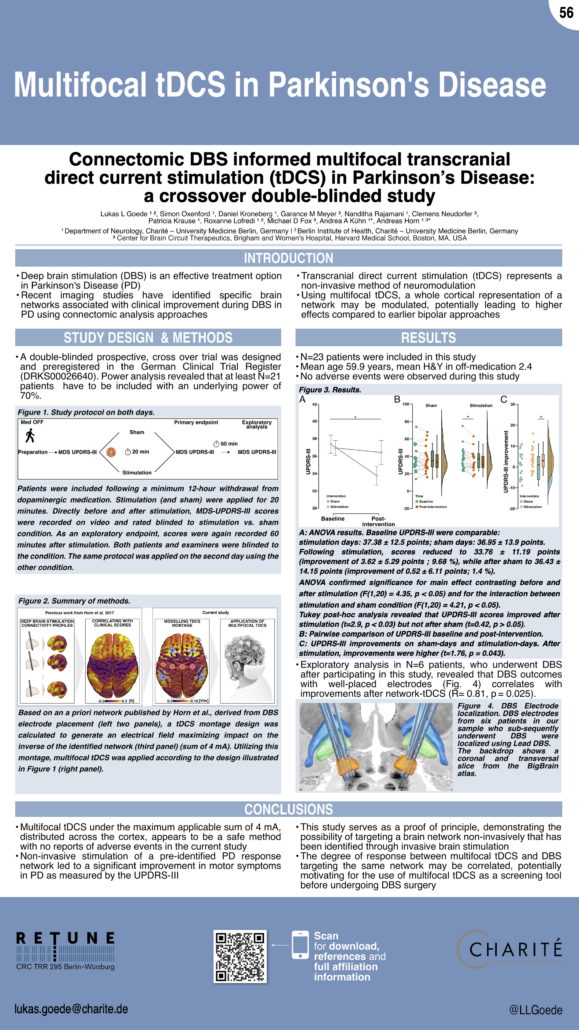
Goede et al. (MDS 2023)
Connectomic DBS informed multifocal transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) in Parkinson’s Disease:
a crossover double-blinded study
Affiliations
Department of Neurology with Experimental Neurology, Charité-Universitätsmedizin Berlin, corporate member of Freie Universität Berlin and Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Berlin, Germany
Berlin Institute of Health at Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, BIH Biomedical Innovation Academy, BIH Charité Junior Clinician Scientist Program, Berlin, Germany
Center for Brain Circuit Therapeutics, Departments of Neurology, Psychiatry, and Radiology, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA
MGH Neurosurgery & Center for Neurotechnology and Neurorecovery (CNTR) at MGH Neurology Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA 02114, USA
Bernstein Center for Computational Neuroscience, Humboldt-Universität, Berlin, Germany
NeuroCure, Exzellenzcluster, Charité-Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Berlin, Germany
DZNE, German Center for Neurodegenerative Diseases, Berlin, Germany
Berlin School of Mind and Brain, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Berlin, Germany
Dr. Goede is participant in the BIH Charité Junior Clinician Scientist Program
funded by the Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, and the Berlin Institute of Health at Charité (BIH).
Dr. Lofredi is participant in the BIH Charité Clinician Scientist Program
funded by the Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, and the Berlin Institute of Health at Charité (BIH).
Funded by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG, German Research Foundation) – Project-ID 424778381 – TRR 295 and Emmy Noether Stipend 410169619 to A.H.
References
[1] Fox MD, Buckner RL, Liu H, Chakravarty MM, Lozano AM, Pascual-Leone A. Resting-state networks link invasive and noninvasive brain stimulation across diverse psychiatric and neurological diseases. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2014;111:E4367–E4375.
[2] Horn A, Reich M, Vorwerk J, et al. Connectivity Predicts deep brain stimulation outcome in Parkinson disease: DBS Outcome in PD. Ann Neurol. 2017;82:67–78.
[3] Sobesky L, Goede L, Odekerken VJJ, et al. Subthalamic and pallidal deep brain stimulation: are we modulating the same network? Brain. 2022;145:251–262.
[4] Fischer DB, Fried PJ, Ruffini G, et al. Multifocal tDCS targeting the resting state motor network increases cortical excitability beyond traditional tDCS targeting unilateral motor cortex. NeuroImage. 2017;157:34–44.
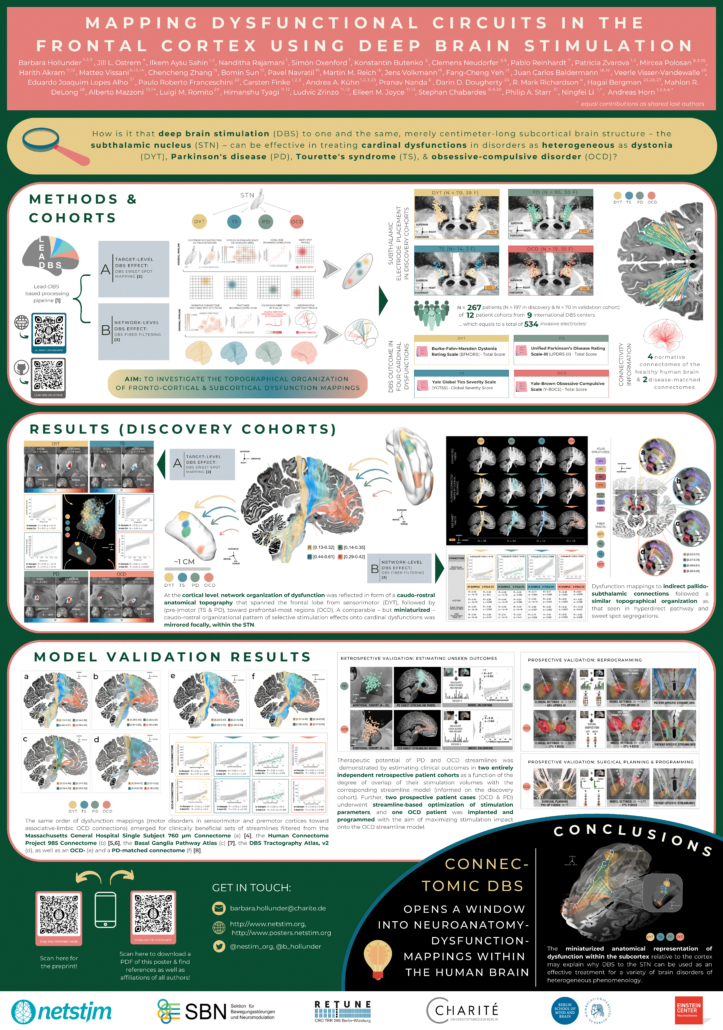
Hollunder et al. (OHBM 2023)
Mapping Dysfunctional Circuits in the Frontal Cortex Using Deep Brain Stimulation
Affiliations
- Department of Neurology, Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Berlin, Germany
- Einstein Center for Neurosciences Berlin, Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Berlin, Germany
- Berlin School of Mind and Brain, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Berlin, Germany
- Movement Disorders and Neuromodulation Centre, Department of Neurology, University of California San Francisco, San Francisco, CA, USA
- Center for Brain Circuit Therapeutics, Department of Neurology, Brigham & Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA
- Department of Neurosurgery, Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA
- Department of Psychiatry and Psychotherapy, Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Berlin, Germany
- Grenoble Alpes, Grenoble, France
- Inserm, U1216, Grenoble Institut des Neurosciences, Grenoble, France
- Psychiatry Department, Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Grenoble Alpes, Grenoble, France
- Department of Clinical and Movement Neurosciences, University College London Queen Square Institute of Neurology, London, UK
- National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery, University College London Queen Square Institute of Neurology, London, UK
- The BioRobotics Institute, Scuola Superiore Sant’Anna, Pisa, Italy
- Department of Excellence in Robotics and AI, Scuola Superiore Sant’Anna, Pisa, Italy
- Department of Neurosurgery, Rujin Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China
- Department of Neurology, University Hospital Würzburg, Würzburg, Germany
- Department of Bioengineering, University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, PA, USA
- Department of Psychiatry and Psychotherapy, Faculty of Medicine and University Hospital Cologne, University of Cologne, Cologne, Germany
- Department of Neurology, Faculty of Medicine and University Hospital Cologne, University of Cologne, Cologne, Germany
- Department of Stereotactic and Functional Neurosurgery, Faculty of Medicine and University Hospital Cologne, University of Cologne, Cologne, Germany
- Clinic of Pain and Functional Neurosurgery, São Paulo, Brazil
- Department of Neurology and Neurosurgery, University of Caxias do Sul, Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil
- NeuroCure Cluster of Excellence, Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Berlin, Germany
- Department of Psychiatry, Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA
- The Edmond and Lily Safra Center for Brain Sciences, The Hebrew University, Jerusalem, Israel
- Department of Medical Neurobiology, Institute of Medical Research Israel-Canada, The Hebrew University, Hassadah Medical School, Jerusalem, Israel
- Department of Neurosurgery, Hadassah Medical Center, Jerusalem, Israel
- Department of Neurology, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, GA, USA
- Parkinson and Movement Disorders Unit, Fondazione IRCCS Istituto Neurologico Carlo Besta, Milan, Italy
- Department of Neurosurgery, Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Grenoble Alpes, Grenoble, France
- Department of Neurological Surgery, University of California San Francisco, San Francisco, CA, USA
References
[1] Neudorfer, C. et al. Lead-DBS v3.0: Mapping deep brain stimulation effects to local anatomy and global networks. Neuroimage 268, 119862 (2023).
[2] Horn, A. et al. Optimal deep brain stimulation sites and networks for cervical vs. generalized dystonia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 119, e2114985119 (2022).
[3] Irmen, F. et al. Left prefrontal connectivity links subthalamic stimulation with depressive symptoms. Ann. Neurol. 87, 962–975 (2020).
[4] Wang, F. et al. In vivo human whole-brain Connectom diffusion MRI dataset at 760 µm isotropic resolution. Sci. Data8, 122 (2021).
[5] Van Essen, D. C. et al. The WU-Minn Human Connectome Project: An overview. Neuroimage 80, 62–79 (2013).
[6] Li, N. et al. A unified connectomic target for deep brain stimulation in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Nat. Commun. 11, 3364 (2020).
[7] Petersen, M. V et al. Holographic reconstruction of axonal pathways in the human brain. Neuron 104, 1056-1064.e3 (2019).
[8] Ewert, S. et al. Toward defining deep brain stimulation targets in MNI space: A subcortical atlas based on multimodal MRI, histology and structural connectivity. Neuroimage 170, 271–282 (2018).
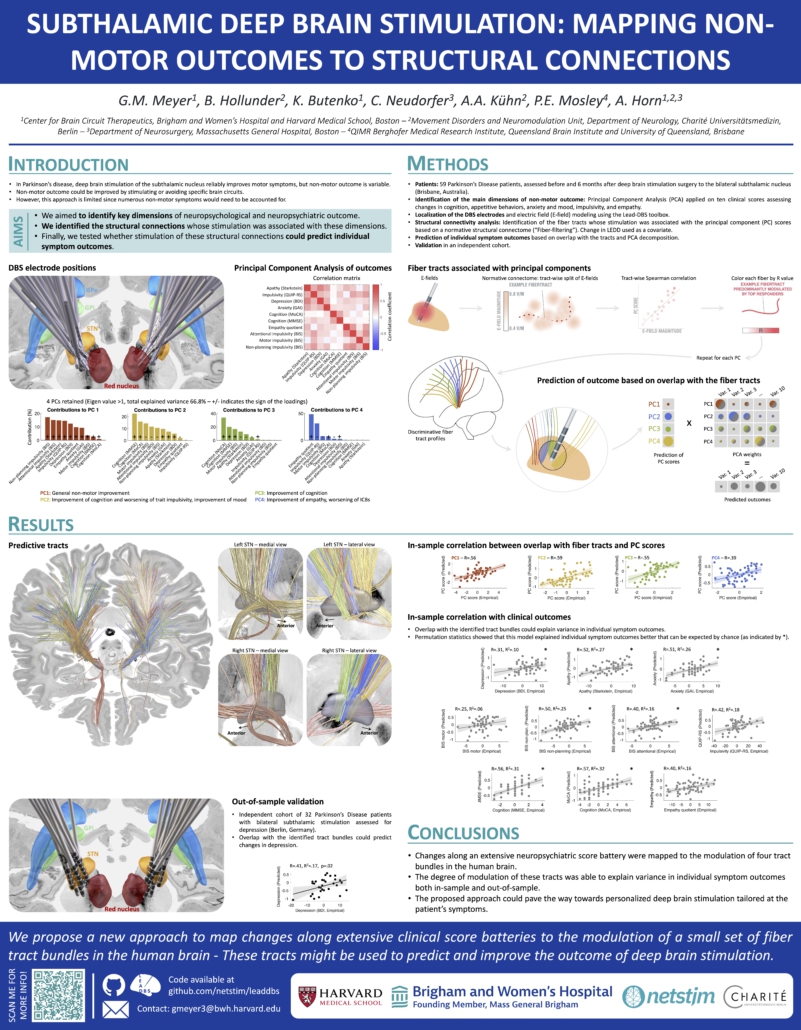
Meyer et al. (OHBM 2023)
Subthalamic Deep Brain Stimulation: Mapping Non-Motor Outcomes to Structural Connections
References
[1] Irmen, F. et al. 2020. Left Prefrontal Connectivity Links Subthalamic Stimulation with Depressive Symptoms. Annals of Neurology 87, 962–975.
[2] Mosley, P.E. et al. 2020. The structural connectivity of subthalamic deep brain stimulation correlates with impulsivity in Parkinson’s. Brain 143, 2235–2254.
[3] Neudorfer, C. et al. 2023. Lead-DBS v3.0: Mapping deep brain stimulation effects to local anatomy and global networks. NeuroImage 268, 119862.
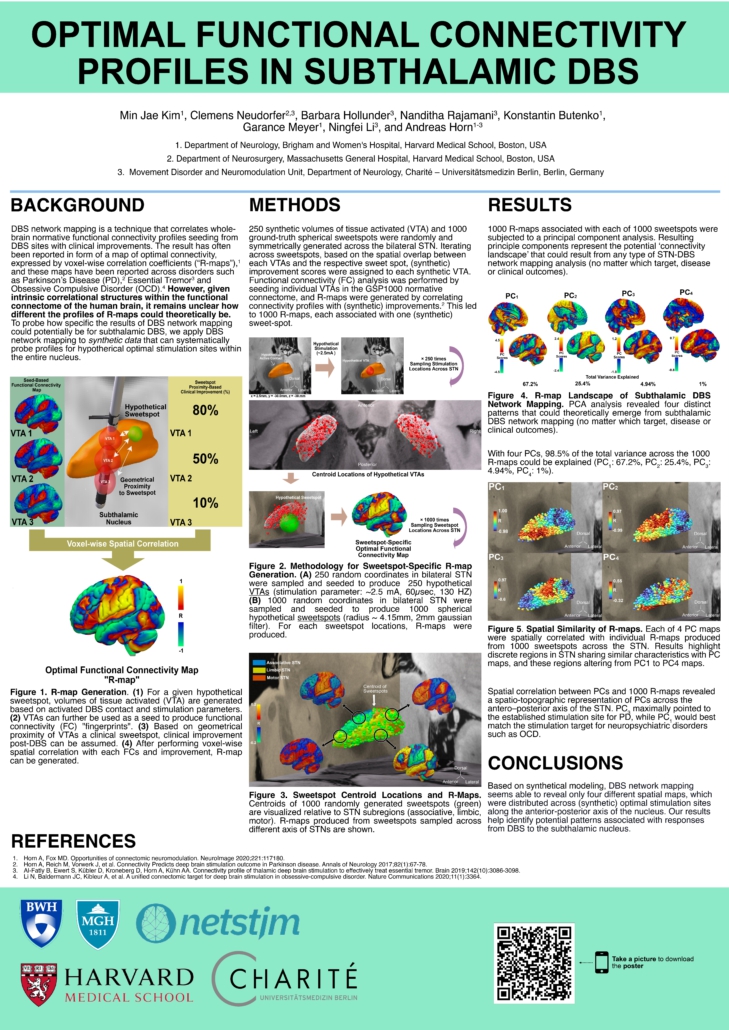
Kim et al. (DBS Society Congress 2023)
Optimal Functional Connectivity Profiles in Subthalamic DBS
References
[1] Horn A, Fox MD. Opportunities of connectomic neuromodulation. NeuroImage 2020;221:117180.
[2] Horn A, Reich M, Vorwerk J, et al. Connectivity Predicts deep brain stimulation outcome in Parkinson disease. Annals of Neurology 2017;82(1):67-78.
[3] Al-Fatly B, Ewert S, Kübler D, Kroneberg D, Horn A, Kühn AA. Connectivity profile of thalamic deep brain stimulation to effectively treat essential tremor. Brain 2019;142(10):3086-3098.
[4] Li N, Baldermann JC, Kibleur A, et al. A unified connectomic target for deep brain stimulation in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Nature Communications 2020;11(1):3364. (2018).
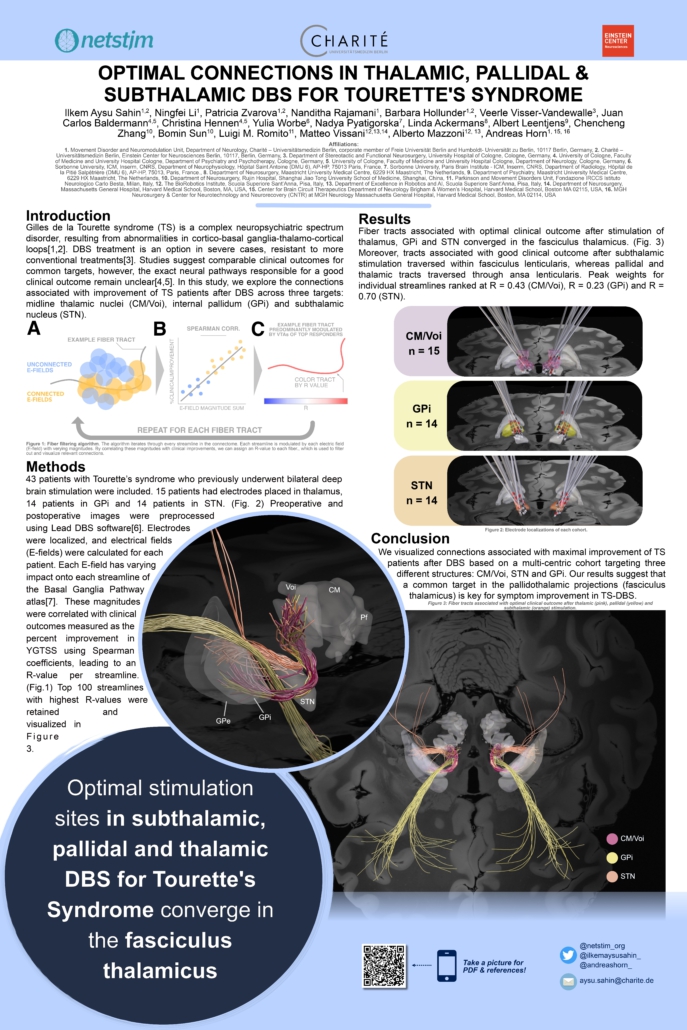
Sahin et al. (DBS Society Congress 2023)
Optimal Connections in Thalamic, Pallidal and Subthalamic DBS for Tourette’s Syndrome
References
[1] Bronfeld, M. & Bar-Gad, I. Tic Disorders: What Happens in the Basal Ganglia? Neuroscientist 19, 101–108 (2013).
[2] Augustine, F. & Singer, H. S. Merging the Pathophysiology and Pharmacotherapy of Tics. Tremor Other Hyperkinet Mov (N Y) 8, 595 (2019).
[3] Billnitzer, A. & Jankovic, J. Current Management of Tics and Tourette Syndrome: Behavioral, Pharmacologic, and Surgical Treatments. Neurotherapeutics 17, 1681–1693 (2020).
[4] Martinez-Ramirez, D. et al. Efficacy and Safety of Deep Brain Stimulation in Tourette Syndrome: The International Tourette Syndrome Deep Brain Stimulation Public Database and Registry. JAMA Neurology 75, 353–359 (2018).
[5] Baldermann, J. C. et al. Deep Brain Stimulation for Tourette-Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Brain Stimulation: Basic, Translational, and Clinical Research in Neuromodulation 9, 296–304 (2016).
[6] Neudorfer, C. et al. Lead-DBS v3.0: Mapping deep brain stimulation effects to local anatomy and global networks. NeuroImage 268, 119862 (2023).
[7] Petersen, M. V. et al. Holographic Reconstruction of Axonal Pathways in the Human Brain. Neuron 104, 1056-1064.e3 (2019).
Hollunder et al. (OHBM & DBS Society Congress 2023)
Symptom Network Modulation of Deep Brain Stimulation in Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
Affiliations
- Department of Neurology, Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Berlin, Germany
- Einstein Center for Neurosciences Berlin, Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Berlin, Germany
- Berlin School of Mind and Brain, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Berlin, Germany
- Center for Brain Circuit Therapeutics, Department of Neurology, Brigham & Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA
- Department of Neurosurgery, Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA
- Biological and Health Psychology, School of Psychology, Universidad Autónoma de Madrid, Spain
- Clinical Brain Networks Group, QIMR Berghofer Medical Research Institute, Herston, Queensland, Australia
- Neurosciences Queensland, St Andrew’s War Memorial Hospital, Spring Hill, Queensland, Australia
- Queensland Brain Institute, University of Queensland, St Lucia, Queensland, Australia
- Australian eHealth Research Centre, CSIRO Health and Biosecurity, Herston, Queensland, Australia
- Department of Clinical and Movement Neurosciences, UCL Queen Square Institute of Neurology, London, UK
- National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery, UCL Queen Square Institute of Neurology, London, UK
- Centre for Mental Health, Swinburne University of Technology, Melbourne, VIC, Australia
- Vincent’s Hospital Melbourne, Melbourne, Australia
- Department of Psychiatry, Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA
- Division of Neurosurgery, Department of Surgery, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada
- Department of Neurosurgery, Hospital Clinico San Carlos, Instituto de Investigacion Sanitaria San Carlos, Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Madrid, Spain
- Laboratory for Clinical Neuroscience, Center for Biomedical Technology, Universidad Politécnica de Madrid, IdISSC, Madrid, Spain
- Centre for Complex Interventions, Centre for Addiction and Mental Health, Toronto, ON, Canada
- Institute of Medical Sciences, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada
- Department of Psychiatry, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada
- Centre for Mental Health, Swinburne University, Melbourne, Australia
- Department of Psychiatry, University of Melbourne, Melbourne, Australia
- Department of Neurosurgery, Brigham & Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA
- NeuroCure Cluster of Excellence, Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Berlin, Germany
- Department of Psychiatry and Psychotherapy, Faculty of Medicine and University Hospital Cologne, University of Cologne, Cologne, Germany
- Johanniter Hospital Oberhausen, EVKLN, Department of Psychiatry, Psychotherapy and Psychosomatics, Oberhausen, Germany
- Department of Stereotactic and Functional Neurosurgery, Faculty of Medicine and University Hospital Cologne, University of Cologne, Cologne, Germany
- Univ Grenoble Alpes, Grenoble, France
- Inserm, U1216, Grenoble Institut des Neurosciences, Grenoble, France
- Department of Psychiatry, Icahn School of Medicine, Mount Sinai Hospital, New York, USA
- Krembil Brain Institute, Toronto, ON, Canada
- Psychiatry Department, CHU Grenoble Alpes, Grenoble, France
- Department of Neurology, Faculty of Medicine and University Hospital Cologne, University of Cologne, Cologne, Germany
References
[1] Figee, M., & Mayberg, H. (2021). The future of personalized brain stimulation. Nature Medicine, 27, 196–197. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-021-01243-7
[2] Baldermann, J. C. et al. (2019). Connectivity profile predictive of effective deep brain stimulation in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Biological Psychiatry, 85(9), 735–743. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2018.12.019
[3] Baldermann, J. C. et al. (2021). Connectomic deep brain stimulation for obsessive-compulsive disorder. Biological Psychiatry, 90(10), 678–688. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2021.07.010
[4] Li, N. et al. (2020). A unified connectomic target for deep brain stimulation in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Nature Communications, 11, 3364. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-16734-3
[5] Hollunder, B. et al. (2022). Toward personalized medicine in connectomic deep brain stimulation. Progress in Neurobiology, 210(210), 102211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2021.102211
[6] Neudorfer, C. et al. Lead-DBS v3.0: Mapping deep brain stimulation effects to local anatomy and global networks. Neuroimage 268, 119862 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2023.119862
[7] Irmen, F. et al. (2020). Left prefrontal connectivity links subthalamic stimulation with depressive symptoms. Annals of Neurology, 87(6), 962–975. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.25734
Zvarova et al. (DBS Society Congress 2023)
A Novel Database Lookup Method for Deep Brain Stimulation Network Mapping
References
[1] Horn, A., Reich, M., Vorwerk, J., Li, N., Wenzel, G., Fang, Q., Schmitz-Hübsch, T., Nickl, R., Kupsch, A., Volkmann, J., Kühn, A.A., Fox, M.D., 2017. Connectivity Predicts deep brain stimulation outcome in Parkinson disease: DBS Outcome in PD. Ann Neurol. 82, 67–78. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.24974
[2] Van Essen, D.C., Ugurbil, K., Auerbach, E., Barch, D., Behrens, T.E.J., Bucholz, R., Chang, A., Chen, L., Corbetta, M., Curtiss, S.W., Della Penna, S., Feinberg, D., Glasser, M.F., Harel, N., Heath, A.C., Larson-Prior, L., Marcus, D., Michalareas, G., Moeller, S., Oostenveld, R., Petersen, S.E., Prior, F., Schlaggar, B.L., Smith, S.M., Snyder, A.Z., Xu, J., Yacoub, E., 2012. The Human Connectome Project: A data acquisition perspective. Neuroimage 62, 2222–2231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.02.018
[3] Ewert, S., Plettig, P., Li, N., Chakravarty, M. M., Collins, D. L., Herrington, T. M., Kühn, A. A., & Horn, A. (2018). Toward defining deep brain stimulation targets in MNI space: A subcortical atlas based on multimodal MRI, histology and structural connectivity. NeuroImage, 170, 271–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.05.015
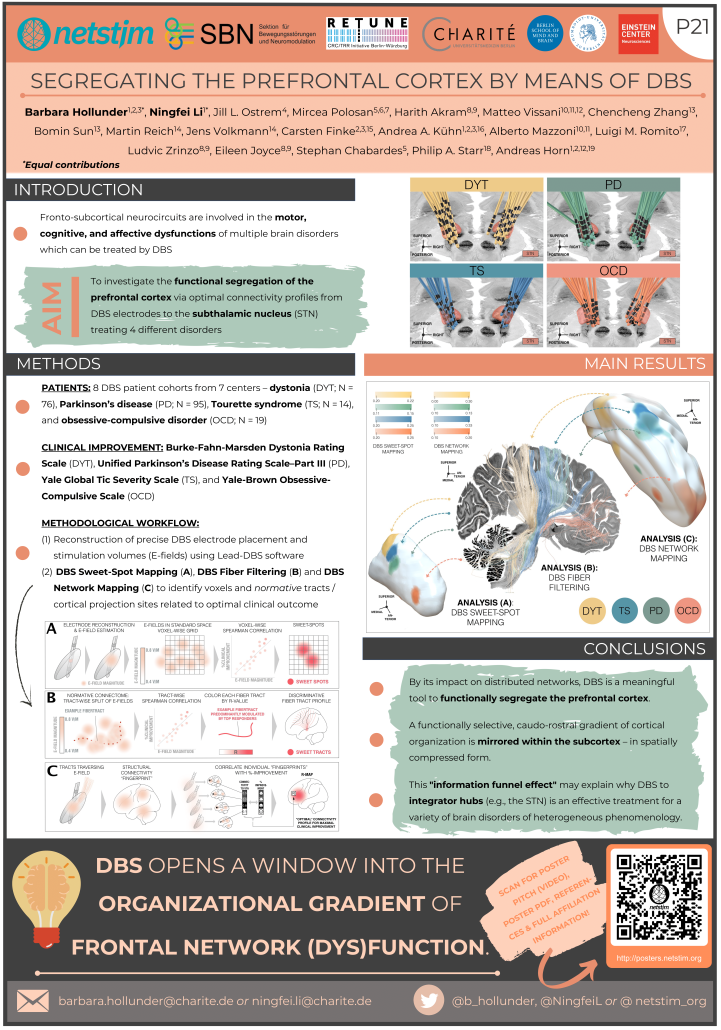
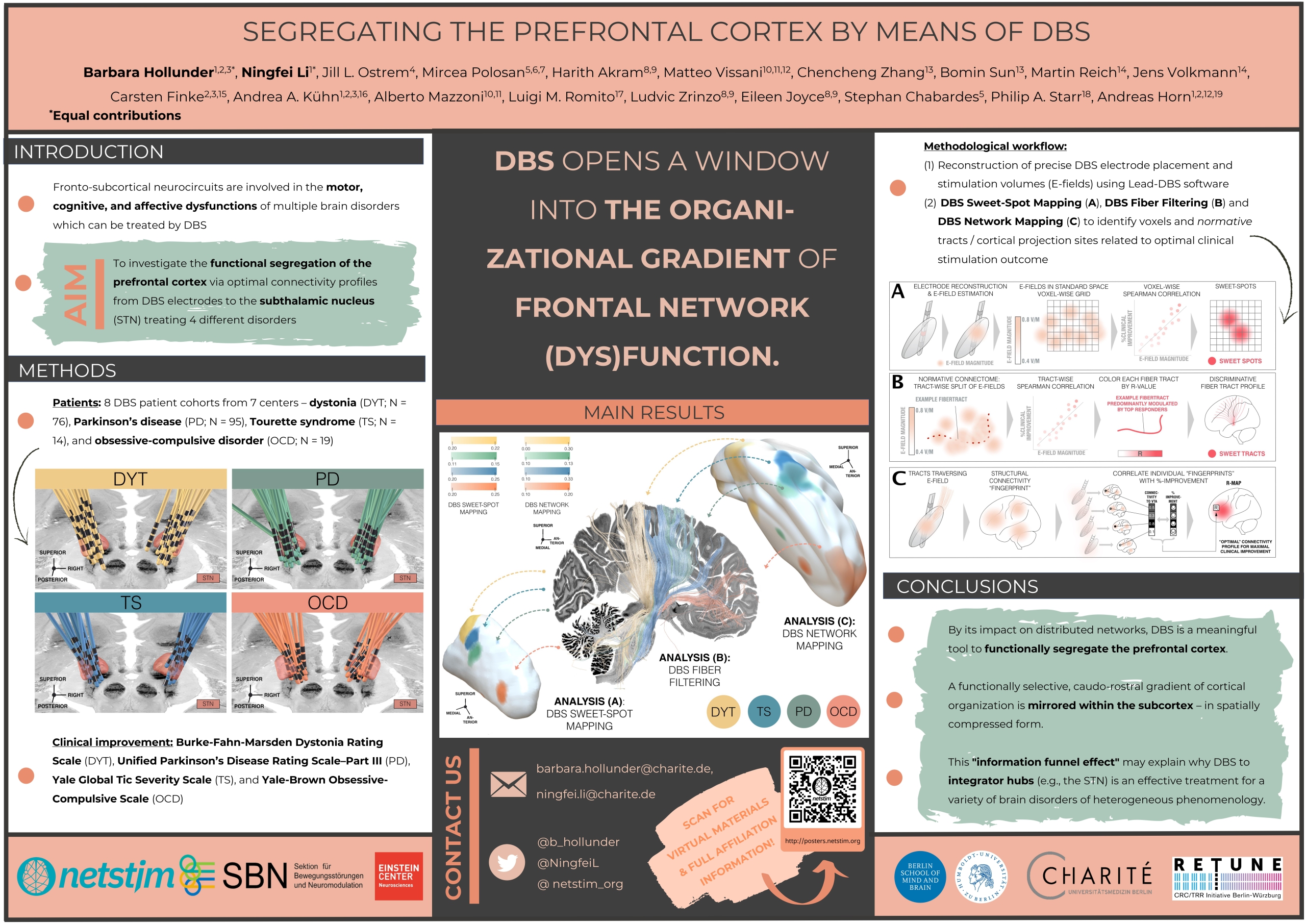
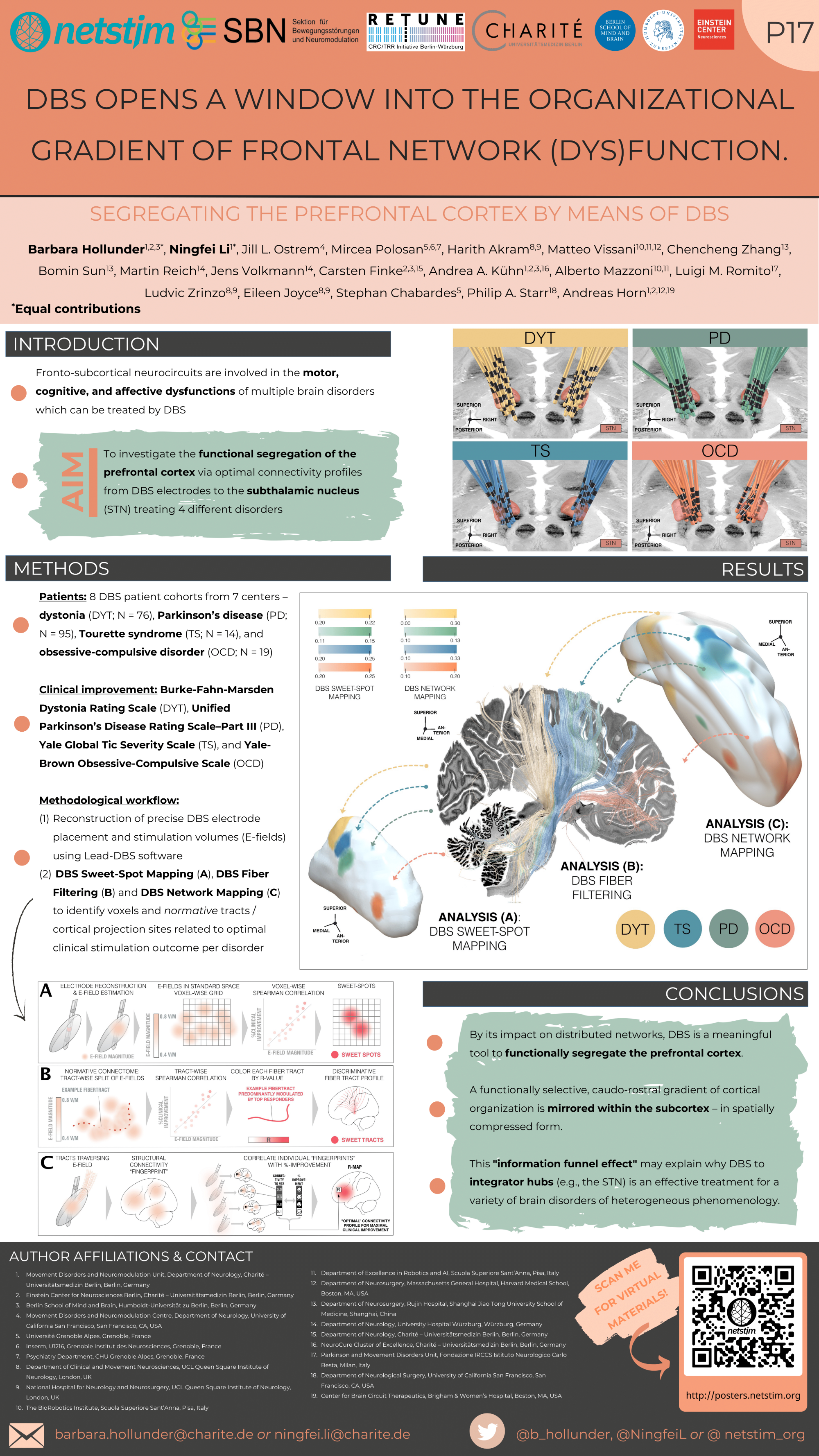
Hollunder & Li et al. (Opto-DBS 2022)
Segregating the Prefrontal Cortex by Means of DBS
Affiliations
- Movement Disorders and Neuromodulation Unit, Department of Neurology, Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Berlin, Germany
- Einstein Center for Neurosciences Berlin, Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Berlin, Germany
- Berlin School of Mind and Brain, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Berlin, Germany
- Movement Disorders and Neuromodulation Centre, Department of Neurology, University of California San Francisco, San Francisco, CA, USA
- Université Grenoble Alpes, Grenoble, France
- Inserm, U1216, Grenoble Institut des Neurosciences, Grenoble, France
- Psychiatry Department, CHU Grenoble Alpes, Grenoble, France
- Department of Clinical and Movement Neurosciences, UCL Queen Square Institute of Neurology, London, UK
- National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery, UCL Queen Square Institute of Neurology, London, UK
- The BioRobotics Institute, Scuola Superiore Sant’Anna, Pisa, Italy
- Department of Excellence in Robotics and AI, Scuola Superiore Sant’Anna, Pisa, Italy
- Department of Neurosurgery, Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA
- Department of Neurosurgery, Rujin Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China
- Department of Neurology, University Hospital Würzburg, Würzburg, Germany
- Department of Neurology, Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Berlin, Germany
- NeuroCure Cluster of Excellence, Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Berlin, Germany
- Parkinson and Movement Disorders Unit, Fondazione IRCCS Istituto Neurologico Carlo Besta, Milan, Italy
- Department of Neurological Surgery, University of California San Francisco, San Francisco, CA, USA
- Center for Brain Circuit Therapeutics, Brigham & Women’s Hospital, Boston, MA, USA
References
Benarroch, E. E. (2008). Subthalamic nucleus and its connections: Anatomic substrate for the network effects of deep brain stimulation. Neurology, 70(21), 1991–1996. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000313022.39329.65
Bonelli, R. M., & Cummings, J. L. (2007). Frontal-subcortical circuitry and behavior. Dialogues in Clinical Neuroscience, 9(2), 141–151. https://doi.org/10.31887/dcns.2007.9.2/rbonelli
Ganos, C., Al-Fatly, B., Fischer, J.-F., Baldermann, J. C., Hennen, C., Visser-Vandewalle, V., … & Horn, A. (2022). A neural network for tics: insights from causal brain lesions and deep brain stimulation, Brain, awac009. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awac009
Haber, S. N., Liu, H., Seidlitz, J., & Bullmore, E. (2021). Prefrontal connectomics: From anatomy to human imaging. Neuropsychopharmacology. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41386-021-01156-6
Haynes, W. I. A., & Haber, S. N. (2013). The organization of prefrontal-subthalamic inputs in primates provides an anatomical substrate for both functional specificity and integration: Implications for basal ganglia models and deep brain stimulation. Journal of Neuroscience, 33(11), 4804–4814. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4674-12.2013
Horn, A., Li, N., Dembek, T. A., Kappel, A., Boulay, C., Ewert, S., Tietze, A., Husch, A., Perera, T., Neumann, W. J., Reisert, M., Si, H., Oostenveld, R., Rorden, C., Yeh, F. C., Fang, Q., Herrington, T. M., Vorwerk, J., & Kühn, A. A. (2019). Lead-DBS v2: Towards a comprehensive pipeline for deep brain stimulation imaging. NeuroImage, 184(July 2018), 293–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2018.08.068
Horn, A., Reich, M., Vorwerk, J., Li, N., Wenzel, G., Fang, Q., Schmitz-Hübsch, T., Nickl, R., Kupsch, A., Volkmann, J., Kühn, A. A., & Fox, M. D. (2017). Connectivity predicts deep brain stimulation outcome in Parkinson disease. Annals of Neurology, 82(1), 67–78. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.24974
Li, N., Baldermann, J. C., Kibleur, A., Treu, S., Akram, H., Elias, G. J. B., Boutet, A., Lozano, A. M., Al-Fatly, B., Strange, B., Barcia, J. A., Zrinzo, L., Joyce, E., Chabardes, S., Visser-Vandewalle, V., Polosan, M., Kuhn, J., Kühn, A. A., & Horn, A. (2020). A unified connectomic target for deep brain stimulation in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Nature Communications, 11, 3364. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-16734-3
Li, N., Hollunder, B., Baldermann, J. C., Kibleur, A., Treu, S., Akram, H., Al-Fatly, B., Strange, B. A., Barcia, J. A., Zrinzo, L., Joyce, E. M., Chabardes, S., Visser-Vandewalle, V., Polosan, M., Kuhn, J., Kühn, A. A., & Horn, A. (2021). A unified functional network target for deep brain stimulation in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Biological Psychiatry, 90(10), 701–713. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2021.04.006
Wang, F., Dong, Z., Tian, Q., Liao, C., Fan, Q., Hoge, W. S., Keil, B., Polimeni, J. R., Wald, L. L., Huang, S. Y., & Setsompop, K. (2021). In vivo human whole-brain Connectom diffusion MRI dataset at 760 µm isotropic resolution. Scientific Data, 8, 122. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-021-00904-z
Hollunder & Li et al. (OHBM 2022)
Segregating the prefrontal cortex by means of DBS
Affiliations
- Movement Disorders and Neuromodulation Unit, Department of Neurology, Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Berlin, Germany
- Einstein Center for Neurosciences Berlin, Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Berlin, Germany
- Berlin School of Mind and Brain, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Berlin, Germany
- Movement Disorders and Neuromodulation Centre, Department of Neurology, University of California San Francisco, San Francisco, CA, USA
- Université Grenoble Alpes, Grenoble, France
- Inserm, U1216, Grenoble Institut des Neurosciences, Grenoble, France
- Psychiatry Department, CHU Grenoble Alpes, Grenoble, France
- Department of Clinical and Movement Neurosciences, UCL Queen Square Institute of Neurology, London, UK
- National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery, UCL Queen Square Institute of Neurology, London, UK
- The BioRobotics Institute, Scuola Superiore Sant’Anna, Pisa, Italy
- Department of Excellence in Robotics and AI, Scuola Superiore Sant’Anna, Pisa, Italy
- Department of Neurosurgery, Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA
- Department of Neurosurgery, Rujin Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China
- Department of Neurology, University Hospital Würzburg, Würzburg, Germany
- Department of Neurology, Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Berlin, Germany
- NeuroCure Cluster of Excellence, Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Berlin, Germany
- Parkinson and Movement Disorders Unit, Fondazione IRCCS Istituto Neurologico Carlo Besta, Milan, Italy
- Department of Neurological Surgery, University of California San Francisco, San Francisco, CA, USA
- Center for Brain Circuit Therapeutics, Brigham & Women’s Hospital, Boston, MA, USA
References
Benarroch, E. E. (2008). Subthalamic nucleus and its connections: Anatomic substrate for the network effects of deep brain stimulation. Neurology, 70(21), 1991–1996. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000313022.39329.65
Bonelli, R. M., & Cummings, J. L. (2007). Frontal-subcortical circuitry and behavior. Dialogues in Clinical Neuroscience, 9(2), 141–151. https://doi.org/10.31887/dcns.2007.9.2/rbonelli
Ganos, C., Al-Fatly, B., Fischer, J.-F., Baldermann, J. C., Hennen, C., Visser-Vandewalle, V., … & Horn, A. (2022). A neural network for tics: insights from causal brain lesions and deep brain stimulation, Brain, awac009. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awac009
Haber, S. N., Liu, H., Seidlitz, J., & Bullmore, E. (2021). Prefrontal connectomics: From anatomy to human imaging. Neuropsychopharmacology. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41386-021-01156-6
Haynes, W. I. A., & Haber, S. N. (2013). The organization of prefrontal-subthalamic inputs in primates provides an anatomical substrate for both functional specificity and integration: Implications for basal ganglia models and deep brain stimulation. Journal of Neuroscience, 33(11), 4804–4814. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4674-12.2013
Horn, A., Li, N., Dembek, T. A., Kappel, A., Boulay, C., Ewert, S., Tietze, A., Husch, A., Perera, T., Neumann, W. J., Reisert, M., Si, H., Oostenveld, R., Rorden, C., Yeh, F. C., Fang, Q., Herrington, T. M., Vorwerk, J., & Kühn, A. A. (2019). Lead-DBS v2: Towards a comprehensive pipeline for deep brain stimulation imaging. NeuroImage, 184(July 2018), 293–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2018.08.068
Horn, A., Reich, M., Vorwerk, J., Li, N., Wenzel, G., Fang, Q., Schmitz-Hübsch, T., Nickl, R., Kupsch, A., Volkmann, J., Kühn, A. A., & Fox, M. D. (2017). Connectivity predicts deep brain stimulation outcome in Parkinson disease. Annals of Neurology, 82(1), 67–78. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.24974
Li, N., Baldermann, J. C., Kibleur, A., Treu, S., Akram, H., Elias, G. J. B., Boutet, A., Lozano, A. M., Al-Fatly, B., Strange, B., Barcia, J. A., Zrinzo, L., Joyce, E., Chabardes, S., Visser-Vandewalle, V., Polosan, M., Kuhn, J., Kühn, A. A., & Horn, A. (2020). A unified connectomic target for deep brain stimulation in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Nature Communications, 11, 3364. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-16734-3
Li, N., Hollunder, B., Baldermann, J. C., Kibleur, A., Treu, S., Akram, H., Al-Fatly, B., Strange, B. A., Barcia, J. A., Zrinzo, L., Joyce, E. M., Chabardes, S., Visser-Vandewalle, V., Polosan, M., Kuhn, J., Kühn, A. A., & Horn, A. (2021). A unified functional network target for deep brain stimulation in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Biological Psychiatry, 90(10), 701–713. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2021.04.006
Wang, F., Dong, Z., Tian, Q., Liao, C., Fan, Q., Hoge, W. S., Keil, B., Polimeni, J. R., Wald, L. L., Huang, S. Y., & Setsompop, K. (2021). In vivo human whole-brain Connectom diffusion MRI dataset at 760 µm isotropic resolution. Scientific Data, 8, 122. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-021-00904-z
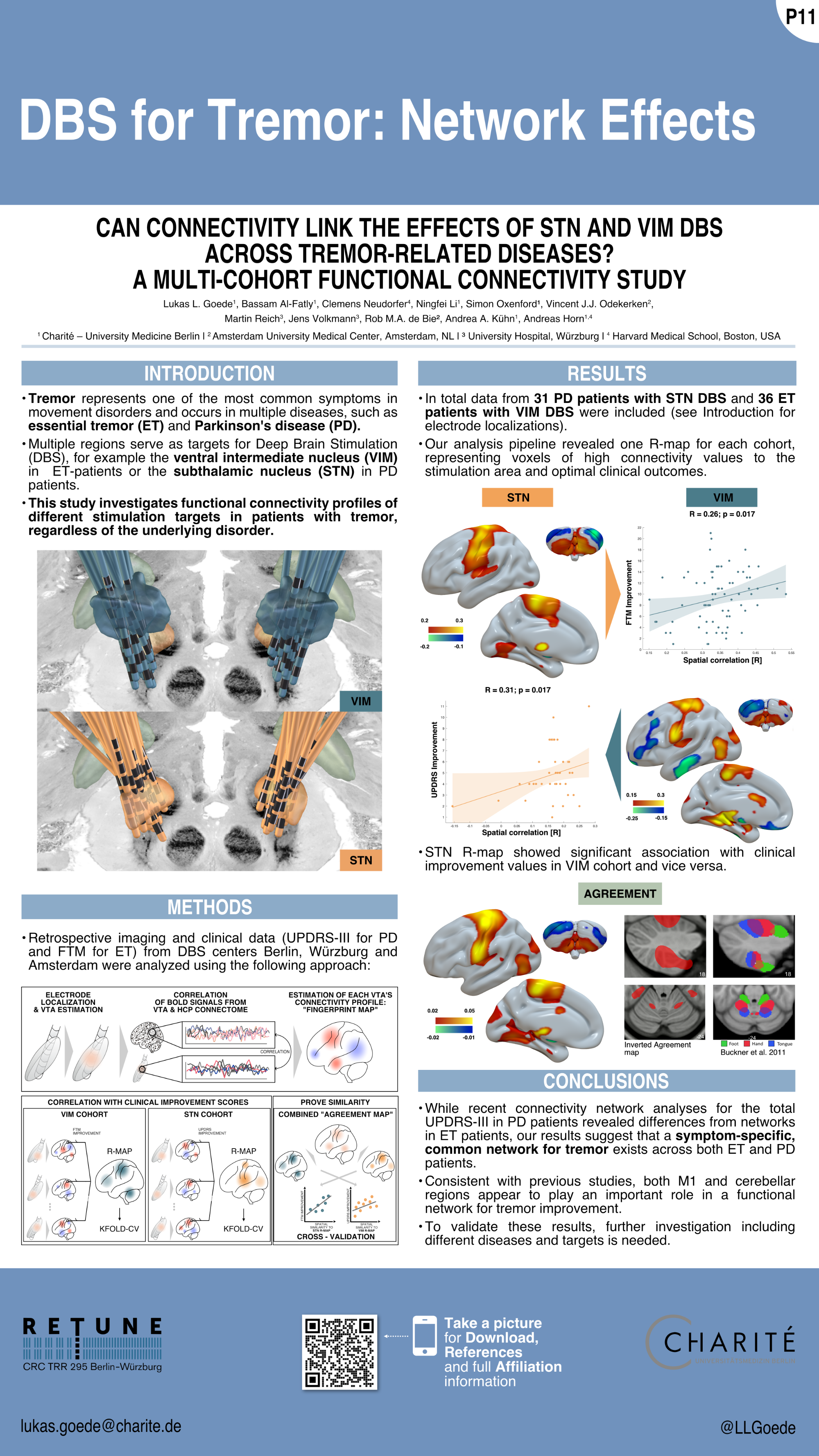
Goede et al. (DBS Expert Summit 2022)
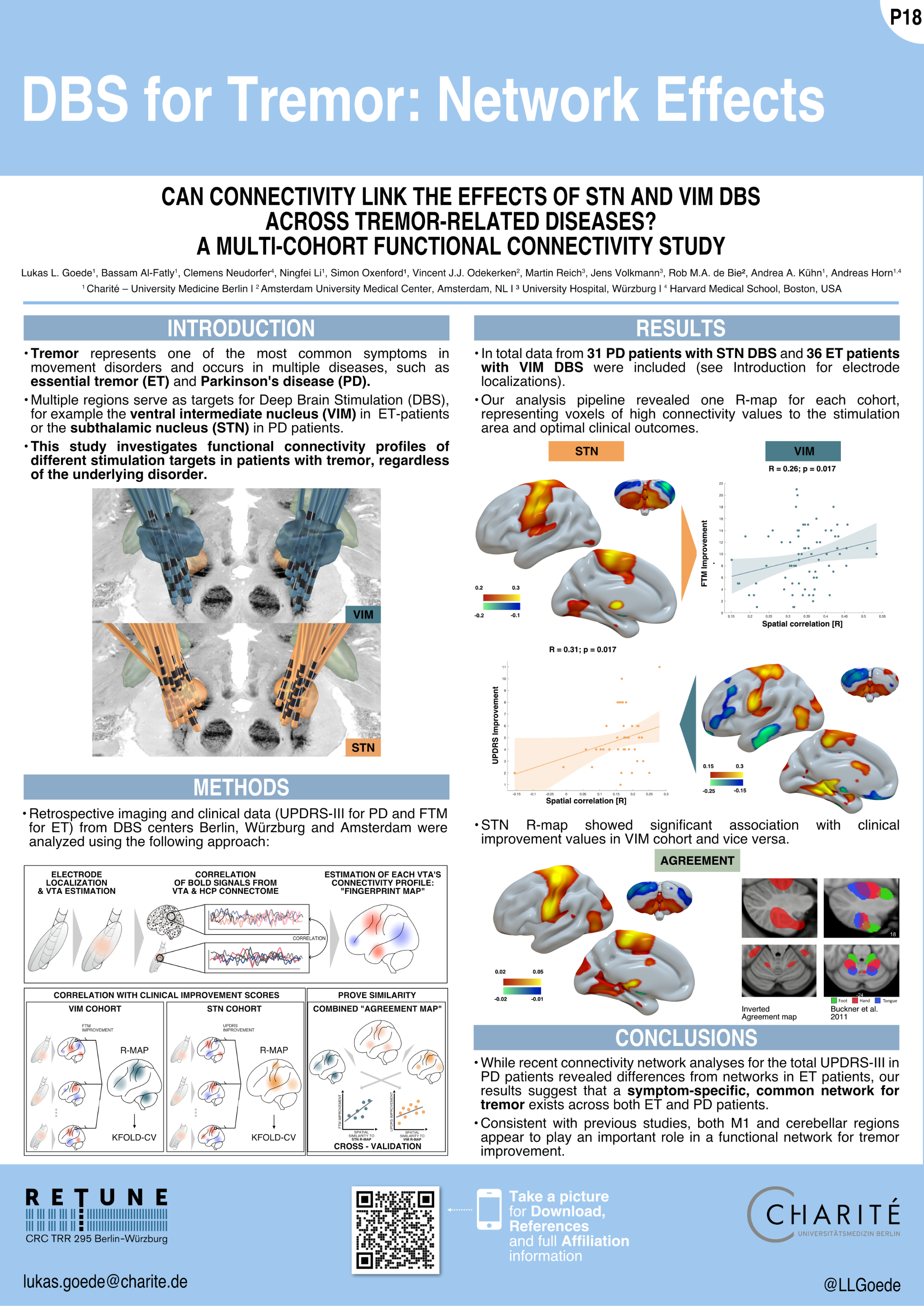
DBS for Tremor: Network Effects
Goede et al. (DGKN 2022)
DBS for Tremor: Network Effects
Affiliations
Lukas L. Goede1,5, Bassam Al-Fatly1, Clemens Neudorfer4, Ningfei Li1, Vincent J.J. Odekerken2, Martin Reich3, Jens Volkmann3, Rob M.A. de Bie2, Andrea A. Kühn1, Andreas Horn1,4
1 Movement Disorder and Neuromodulation Unit, Department of Neurology, Charité Campus Mitte, Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Berlin, Germany
2 Department of Neurology, Amsterdam University Medical Center, Amsterdam, The Netherlands
3 Department of Neurology, University Clinic of Würzburg, Würzburg, Germany
4 Center for Brain Circuit Therapeutics, Department of Neurology Brigham & Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, United States; MAMGH Neurosurgery & Center for Neurotechnology and Neurorecovery (CNTR) at MGH Neurology, Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, United States
5 BIH – Berlin Institute of Health at Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin,
BIH Biomedical Innovation Academy, BIH Charité Junior Clinician Scientist Program, Charitéplatz 1, 10117 Berlin, Germany
References
Deuschl G, Bain P, Brin M. Consensus Statement of the Movement Disorder Society on Tremor. Mov Disord. 2008 Oct 20;13(S3):2–23.
Horn A, Li N, Dembek TA, Kappel A, Boulay C, Ewert S, et al. Lead-DBS v2: Towards a comprehensive pipeline for deep brain stimulation imaging. NeuroImage. 2019 Jan;184:293–316.
Horn A, Reich M, Vorwerk J, Li N, Wenzel G, Fang Q, et al. Connectivity Predicts deep brain stimulation outcome in Parkinson disease: DBS Outcome in PD. Ann Neurol. 2017 Jul;82(1):67–78.
Buckner RL, Krienen FM, Castellanos A, Diaz JC, Yeo BTT. The organization of the human cerebellum estimated by intrinsic functional connectivity. Journal of Neurophysiology. 2011 Nov;106(5):2322–45.
Middlebrooks EH, Okromelidze L, Wong JK, et al. Connectivity Correlates Predicting Deep Brain Stimulation Outcome in Essential Tremor: Evidence for a common treatment pathway. NeuroImage Clin. 2021.
Hollunder & Li et al. (DBS Expert Summit 2022)
Segregating the prefrontal cortex by means of DBS
References
Benarroch, E. E. (2008). Subthalamic nucleus and its connections: Anatomic substrate for the network effects of deep brain stimulation. Neurology, 70(21), 1991–1996. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000313022.39329.65
Bonelli, R. M., & Cummings, J. L. (2007). Frontal-subcortical circuitry and behavior. Dialogues in Clinical Neuroscience, 9(2), 141–151. https://doi.org/10.31887/dcns.2007.9.2/rbonelli
Ganos, C., Al-Fatly, B., Fischer, J.-F., Baldermann, J. C., Hennen, C., Visser-Vandewalle, V., … & Horn, A. (2022). A neural network for tics: insights from causal brain lesions and deep brain stimulation, Brain, awac009. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awac009
Haber, S. N., Liu, H., Seidlitz, J., & Bullmore, E. (2021). Prefrontal connectomics: From anatomy to human imaging. Neuropsychopharmacology. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41386-021-01156-6
Haynes, W. I. A., & Haber, S. N. (2013). The organization of prefrontal-subthalamic inputs in primates provides an anatomical substrate for both functional specificity and integration: Implications for basal ganglia models and deep brain stimulation. Journal of Neuroscience, 33(11), 4804–4814. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4674-12.2013
Horn, A., Li, N., Dembek, T. A., Kappel, A., Boulay, C., Ewert, S., Tietze, A., Husch, A., Perera, T., Neumann, W. J., Reisert, M., Si, H., Oostenveld, R., Rorden, C., Yeh, F. C., Fang, Q., Herrington, T. M., Vorwerk, J., & Kühn, A. A. (2019). Lead-DBS v2: Towards a comprehensive pipeline for deep brain stimulation imaging. NeuroImage, 184(July 2018), 293–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2018.08.068
Horn, A., Reich, M., Vorwerk, J., Li, N., Wenzel, G., Fang, Q., Schmitz-Hübsch, T., Nickl, R., Kupsch, A., Volkmann, J., Kühn, A. A., & Fox, M. D. (2017). Connectivity predicts deep brain stimulation outcome in Parkinson disease. Annals of Neurology, 82(1), 67–78. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.24974
Li, N., Baldermann, J. C., Kibleur, A., Treu, S., Akram, H., Elias, G. J. B., Boutet, A., Lozano, A. M., Al-Fatly, B., Strange, B., Barcia, J. A., Zrinzo, L., Joyce, E., Chabardes, S., Visser-Vandewalle, V., Polosan, M., Kuhn, J., Kühn, A. A., & Horn, A. (2020). A unified connectomic target for deep brain stimulation in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Nature Communications, 11, 3364. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-16734-3
Li, N., Hollunder, B., Baldermann, J. C., Kibleur, A., Treu, S., Akram, H., Al-Fatly, B., Strange, B. A., Barcia, J. A., Zrinzo, L., Joyce, E. M., Chabardes, S., Visser-Vandewalle, V., Polosan, M., Kuhn, J., Kühn, A. A., & Horn, A. (2021). A unified functional network target for deep brain stimulation in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Biological Psychiatry, 90(10), 701–713. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2021.04.006
Wang, F., Dong, Z., Tian, Q., Liao, C., Fan, Q., Hoge, W. S., Keil, B., Polimeni, J. R., Wald, L. L., Huang, S. Y., & Setsompop, K. (2021). In vivo human whole-brain Connectom diffusion MRI dataset at 760 µm isotropic resolution. Scientific Data, 8, 122. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-021-00904-z
Mana et al. (DBS Expert Summit 2022)
Instrumental activities of daily living improve in Parkinson’s Disease after STN DBS
References
Brennan, L., Siderowf, A., Rubright, J.D., Rick, J., Dahodwala, N., Duda, J.E., Hurtig, H., Stern, M., Xie, S.X., Rennert, L., Karlawish, J., Shea, J.A., Trojanowski, J.Q., and Weintraub, D. (2016a). Development and initial testing of the Penn Parkinson’s Daily Activities Questionnaire. Mov Disord 31, 126-134. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.2633
Brennan, L., Siderowf, A., Rubright, J.D., Rick, J., Dahodwala, N., Duda, J.E., Hurtig, H., Stern, M., Xie, S.X., Rennert, L., Karlawish, J., Shea, J.A., Trojanowski, J.Q., and Weintraub, D. (2016b). The Penn Parkinson’s Daily Activities Questionnaire-15: Psychometric properties of a brief assessment of cognitive instrumental activities of daily living in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 25, 21-26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2016.02.020
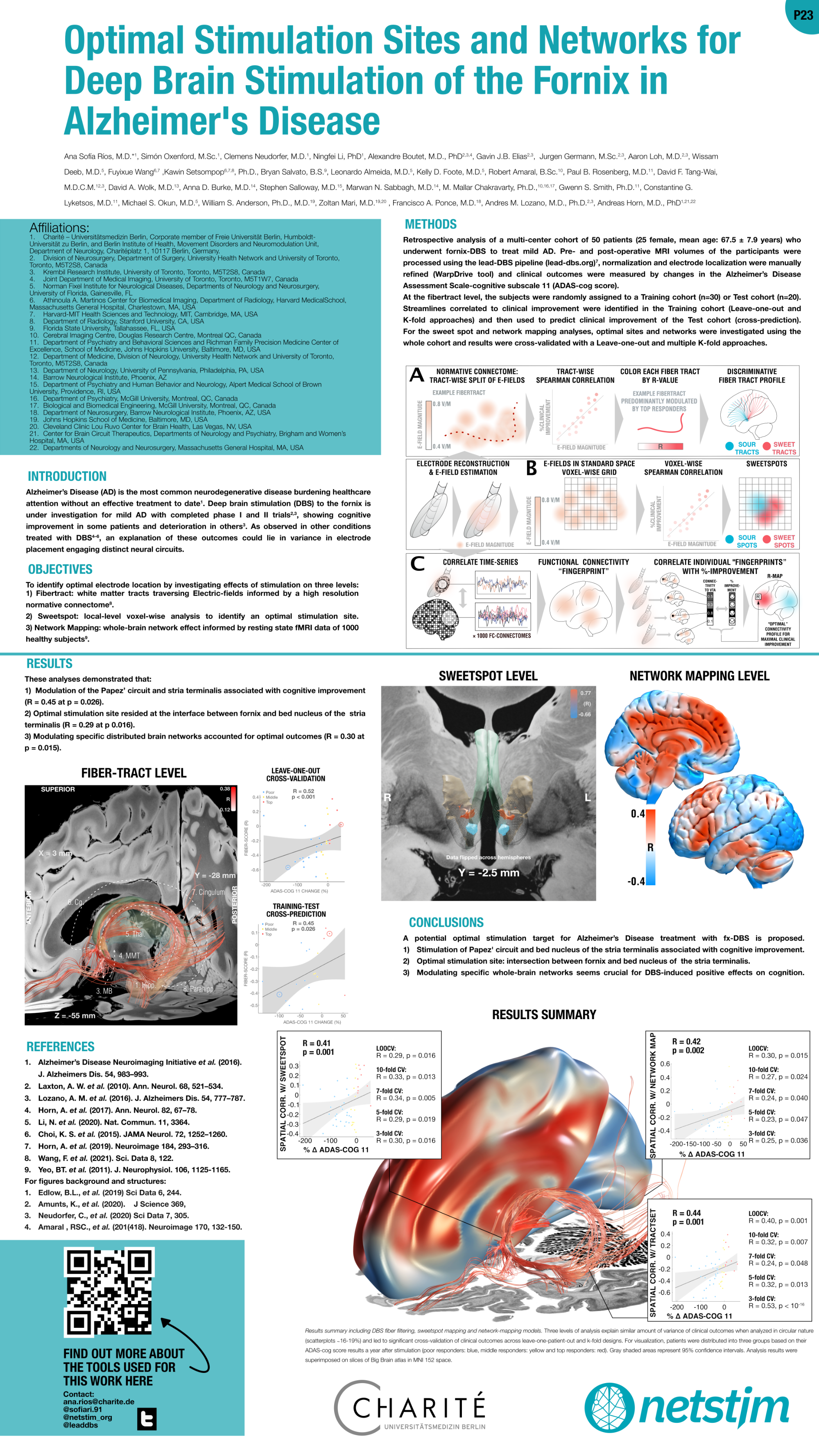
Rios et al. (DBS Expert Summit 2022)
Optimal stimulation sites and networks for DBS of the fornix in Alzheimer’s Diesease
References
Chen, Guangyu et al. “Staging Alzheimer’s Disease Risk by Sequencing Brain Function and Structure, Cerebrospinal Fluid, and Cognition Biomarkers.” Journal of Alzheimer’s disease : JAD vol. 54,3 (2016): 983-993. doi:10.3233/JAD-160537
Laxton, Adrian W et al. “A phase I trial of deep brain stimulation of memory circuits in Alzheimer’s disease.” Annals of neurology vol. 68,4 (2010): 521-34. doi:10.1002/ana.22089
Lozano, Andres M et al. “A Phase II Study of Fornix Deep Brain Stimulation in Mild Alzheimer’s Disease.” Journal of Alzheimer’s disease : JAD vol. 54,2 (2016): 777-87. doi:10.3233/JAD-160017
Horn, Andreas et al. “Connectivity Predicts deep brain stimulation outcome in Parkinson disease.” Annals of neurology vol. 82,1 (2017): 67-78. doi:10.1002/ana.24974
Li, Ningfei et al. “A unified connectomic target for deep brain stimulation in obsessive-compulsive disorder.” Nature communicationsvol. 11,1 3364. 3 Jul. 2020, doi:10.1038/s41467-020-16734-3
Choi, Ki Sueng et al. “Mapping the “Depression Switch” During Intraoperative Testing of Subcallosal Cingulate Deep Brain Stimulation.” JAMA neurology vol. 72,11 (2015): 1252-60. doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2015.2564
Horn, Andreas et al. “Lead-DBS v2: Towards a comprehensive pipeline for deep brain stimulation imaging.” NeuroImage vol. 184 (2019): 293-316. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2018.08.068
Wang, Fuyixue et al. “In vivo human whole-brain Connectom diffusion MRI dataset at 760 µm isotropic resolution.” Scientific data vol. 8,1 122. 29 Apr. 2021, doi:10.1038/s41597-021-00904-z
Yeo, B T Thomas et al. “The organization of the human cerebral cortex estimated by intrinsic functional connectivity.” Journal of neurophysiology vol. 106,3 (2011): 1125-65. doi:10.1152/jn.00338.2011
For figure background and structures
Edlow, Brian L et al. “7 Tesla MRI of the ex vivo human brain at 100 micron resolution.” Scientific data vol. 6,1 244. 30 Oct. 2019, doi:10.1038/s41597-019-0254-8
Amunts, Katrin et al. “Julich-Brain: A 3D probabilistic atlas of the human brain’s cytoarchitecture.” Science (New York, N.Y.)vol. 369,6506 (2020): 988-992. doi:10.1126/science.abb4588
Neudorfer, Clemens et al. “A high-resolution in vivo magnetic resonance imaging atlas of the human hypothalamic region.” Scientific datavol. 7,1 305. 15 Sep. 2020, doi:10.1038/s41597-020-00644-6
Amaral, Robert S C et al. “Manual segmentation of the fornix, fimbria, and alveus on high-resolution 3T MRI: Application via fully-automated mapping of the human memory circuit white and grey matter in healthy and pathological aging.” NeuroImage vol. 170 (2018): 132-150. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.10.027