Three months into 2018, there have been several studies that used Lead-DBS to answer very interesting questions briefly summarized below.
1.
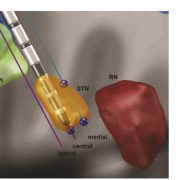
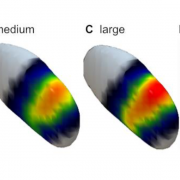
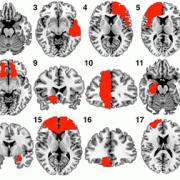
Siobhan Ewert and Todd Herrington could recently show that automated segmentations of the STN and GPi performed with Lead-DBS are nearly as precise as manual expert segmentations of the same structures in both a high-definition MRI sample as well as a “typical clinical” quality sample. In total, they ran >11.000 nonlinear brain deformations and segmented 120 brains manually to evaluate i) which deformation algorithm & preset yields best results and ii) how much error is still obtained when using the best strategy. Their optimal normalization strategy has now become the default preset of Lead-DBS.
2.
Roxanne Lofredi and
Andrea A Kühn have demonstrated that movement velocity is encoded in subthalamic gamma bursts in a recent article that then applied the subcortical electrophysiology mapping (SEM) concept based on electrode localizations performed with Lead-DBS to localize the origin of this gamma activity.
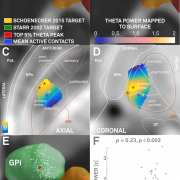
3. Along the same lines: Xinyi Geng and
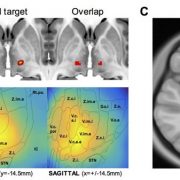
Shouyan Wang have published a paper to put intraoperative LFP findings into an anatomical context following the same (SEM) concept. In their paper, they indirectly replicate main findings of two other recent studies
by
Bernadette van Wijk and Vladimir Litvak (which had already extended the concept to PAC and High-frequency oscillations)
that used Lead-DBS to localize beta power within the STN. The work by Geng et al. further extends beyond these and for instance includes space-relationships for theta and gamma power.
Further info on the idea of “Subcortical Electrophysiology Mapping (SEM)” may be found in our blog post (
http://www.lead-dbs.org/?p=2301) or knowledge-base article (
http://www.lead-dbs.org/?page_id=2403).
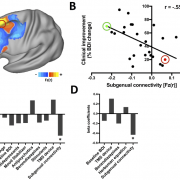
4. Franz Hell and Kai Bötzel published a very interesting study using drift-diffusion models, joint LFP- and EEG-recordings, as well as interventional DBS. Based on their findings, they propose that “motor and executive control networks with complementary oscillatory mechanisms are tonically active, react to stimuli and release inhibition at the response when uncertainty is resolved and return to their default state afterwards.” Lead-DBS was used to localize electrodes implanted to the sensorimotor functional zone of the STN.
5. Canan Peisker and Jens Kuhn published a study of NAc-DBS to treat substance use disorder. They used Lead-DBS to localize the electrodes implanted to the accumbens and investigated wether delay discounting would be modulated by NAc-DBS and concluded to the null-hypothesis.
6.
Philip E Mosley and
Alistair Perry published both a case report (persistence of mania after cessation of STN DBS) and a larger study that involved electrode localizations made with Lead-DBS. The latter represents a comprehensive study about the relationship between non-motor (side) effects of DBS and electrode placement.